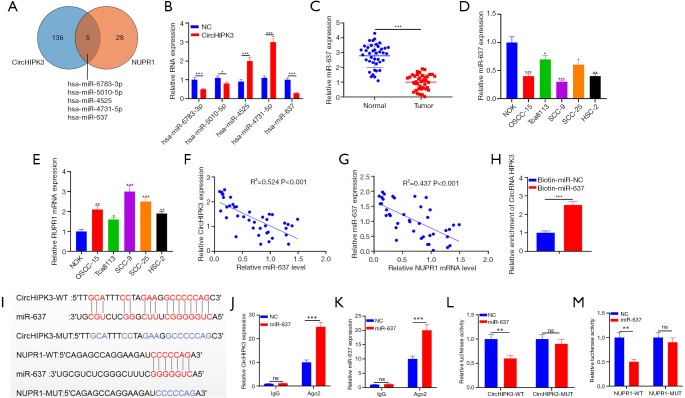
Figure 4.
Targeting the relationships among circHIPK3, NUPR1, and miR-637. (A) The miRNA targets of circHIPK3 and NUPR1 are analyzed by Starbase, and five miRNAs are found to contain conserved binding sites to circHIPK3 and NUPR1; (B) QRT-PCR is used to detect expressions of five miRNAs in overexpressed cells; (C) QRT-PCR is used to detect expressions of miR-637 in OSCC tissues and normal tissues adjacent to cancer; (D,E) QRT-PCR is used to detect miR-637 and NUPR1 expression in NOK and OSCC-15, Tca8113, SCC-9, SCC-25 and HSC-2. (F,G) Pearson correlation analysis is used to detect the correlation between miR-637 and circHIPK3, miR-637, and NUPR1 in OSCC tissues; (H) the relative level of circHIPK3 in biotin-labeled miR-637 or NC-captured cell lysates is detected by an RNA pull-down assay; (I) the binding relationship between miR-637, circHIPK3, and NUPR1; (J,K) the binding of circHIPK3 and NUPR1 to Ago2 antibody in SCC-9 cells is detected by the RIP method; (L,M) the binding relationship between miR-637 and circHIPK3, and miR-637 and NUPR1 in SCC-9 cells is confirmed by dual luciferase reporter gene analysis. nsP>0.05, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. circHIPK3, circular RNA HIPK3; miR-637, microRNA-637; NUPR1, Nucleoprotein 1; OSCC, oral squamous cell carcinoma; QRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR.