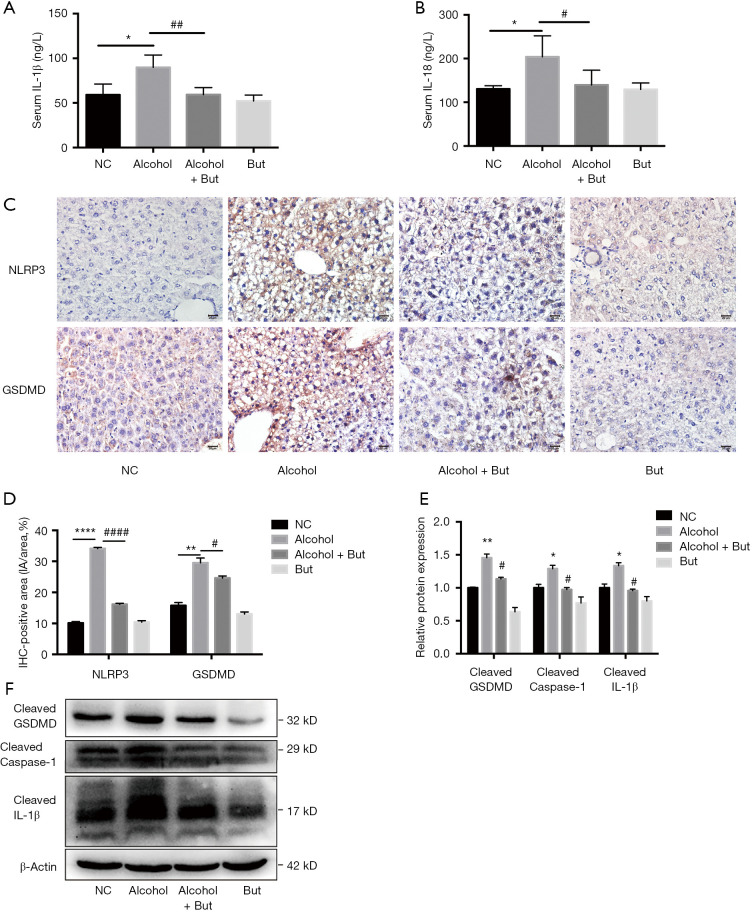
Figure 2.
Butyrate improved alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) via inhibiting the NLRP3-gasdermin D (GSDMD) signaling pathway. (A) Serum IL-1β and (B) serum IL-18 levels were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n=5 per group). (C,D) The expression levels of NLRP3 and GSDMD in the liver were detected by immunohistochemistry (n=3 per group). Scale bar =20 µm. (E,F) The protein expression levels of cleaved GSDMD, caspase-1, and IL-1β were detected by western blot (n=3 per group). Normal control (NC), Alcohol + Butyrate (Alcohol + But), Butyrate (But). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 alcohol group vs. NC group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ####P<0.0001 alcohol + butyrate group vs. alcohol group.