Figure 1.
OIP5-AS1 is enriched in developing cardiac muscle, and is altered during cardiac disease
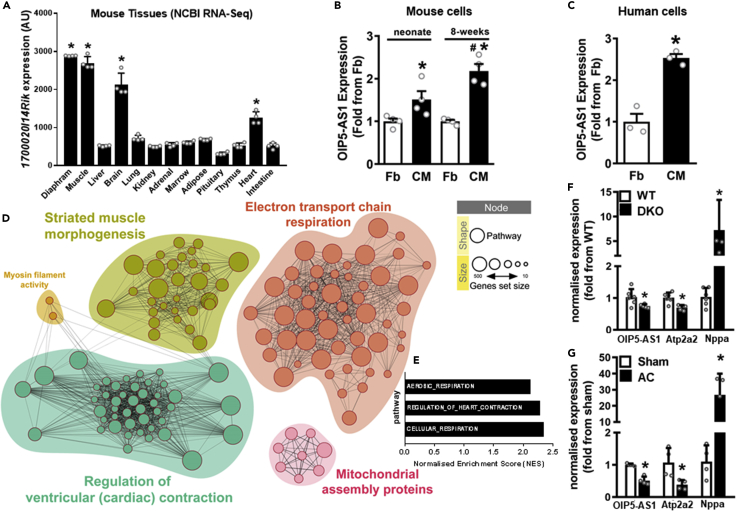
(A) Expression of OIP5-AS1 across mouse tissues sourced from NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO, GSE24207), n = 4/group, mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.001 from liver expression.
(B and C) (B) Expression of OIP5-AS1 as determined by RNA-sequencing in fibroblasts (Fb) and cardiomyocytes (CMs) digested from mouse hearts of neonate and 8-week old mice (n = 4/group, mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05 versus neonate Fb; #p < 0.05 versus neonate CM) from GEO deposited dataset GSE95764, and in (C) Fb and CM differentiated from human iPSCs (n = 3/group, mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05 versus Fb).
(D) Network analysis of genes sets correlated with OIP5-AS1 expression as determined by RNA-sequencing in mouse cardiomyocytes versus fibroblasts from data sets in panel C. Enriched networks include cardiac contraction, muscle morphogenesis and mitochondrial pathways (assembly and electron transport chain (ETC)). For a description of each code shown within the nodes, see Table S2.
(E) Bar graph depicting most highly enriched pathways associated with OIP5-AS1 expression in mouse cardiomyocytes.
(F and G) (F) qPCR determined expression of OIP5-AS1, Atp2a2 (SERCA2) and Nppa (ANP) in hearts from WT or utrophin/dystrophin double KO (DKO) male mice (n = 8/group, mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05 versus WT) (Chen et al., 2017), and (G) WT male mice that have undergone sham or aortic constriction (AC); n = 4–6/group, mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05 versus sham). For A, B, C, F and G, a non-parametric one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons correction (Dunnet's) was used.