Figure 5: Tunnels are active mediators of inflammation in HS and are therapeutically targetable.
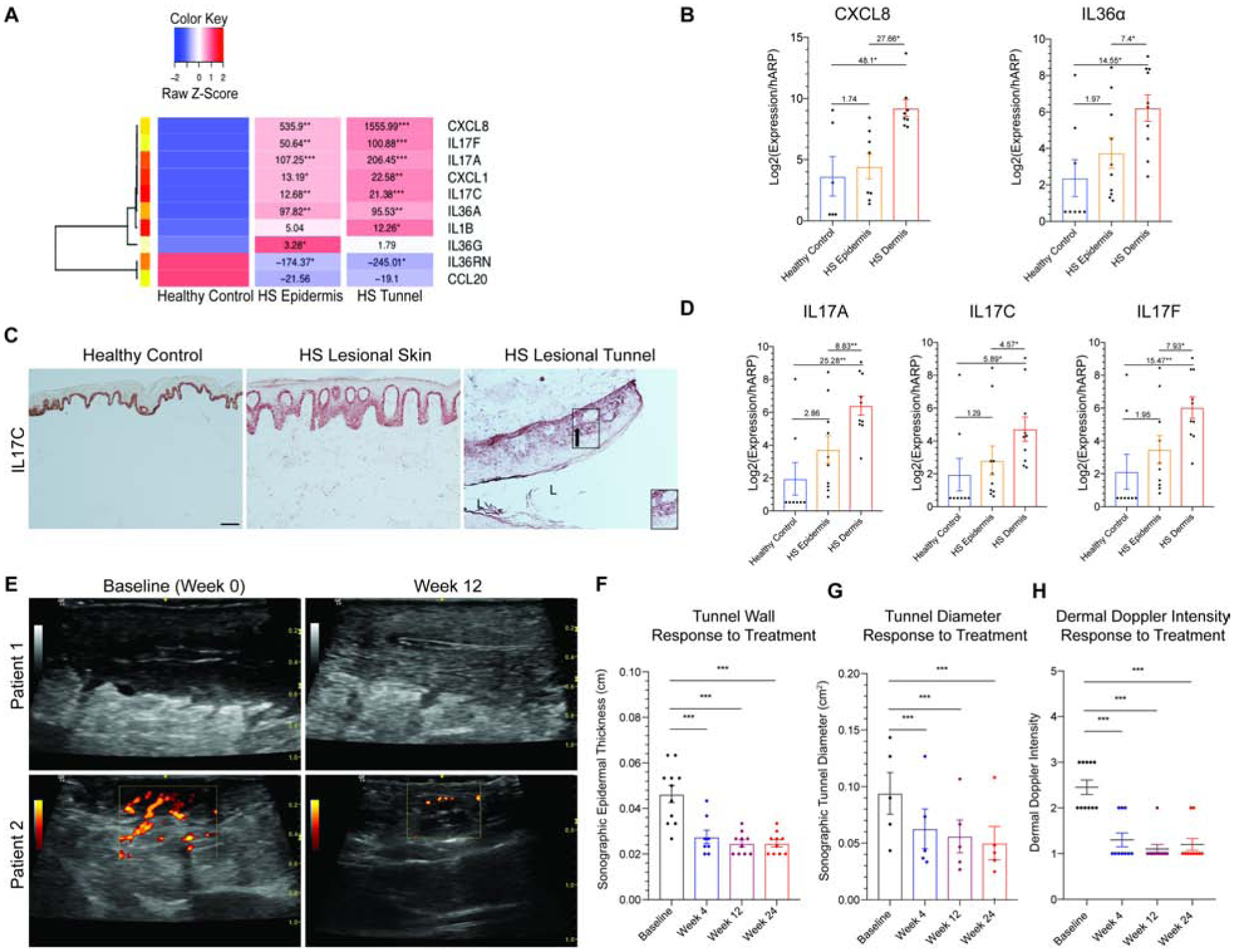
(A) Heatmap of supervised clustering of pro-inflammatory mediators in bisected specimens of HS skin containing healthy controls (n=6), epidermis/superficial dermis (n=8) or deep dermis containing epithelialized tunnels (n=8). Known pro-inflammatory mediators are highest in dermal (tunnel) specimens compared to epidermis/superficial dermis and normal healthy controls. FCH is shown with *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 relative to healthy controls (B) RT-PCR demonstrates elevated expression of targetable cytokines in HS dermal tunnels tunnels (HS Dermis) compared to the overlying epidermis and healthy controls, relative to the total amount of RNA recovered. There is a significant elevation of cytokines in HS tunnels compared to the overlying epidermis. FCH is shown. (C) Healthy control epidermis illustrates IL-17C expression only in the basal keratinocytes. The gradient of IL-17C expression (black arrow) in epithelialized dermal tunnels also recapitulates the gradient seen in psoriasiform epithelium, with greatest expression in the basal layer with reduction of expression towards the lumen of tunnels (L). Scale Bar, 100μm. Arrow indicates direction of IL-17C gradient. (D) Tunnels in HS dermis express IL-17 family cytokines. (E) Doppler Ultrasonography representing reduction in tunnel diameter and doppler intensity following 12 weeks of treatment with IL-17 receptor antagonist. (F) There is a significant decrease in tunnel wall (G) tunnel diameter and (H) dermal doppler intensity following treatment with IL-17 receptor antagonist. Decrease in tunnel inflammation is seen as early as 4 weeks. Results are the mean ± SEM, FCH is shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
