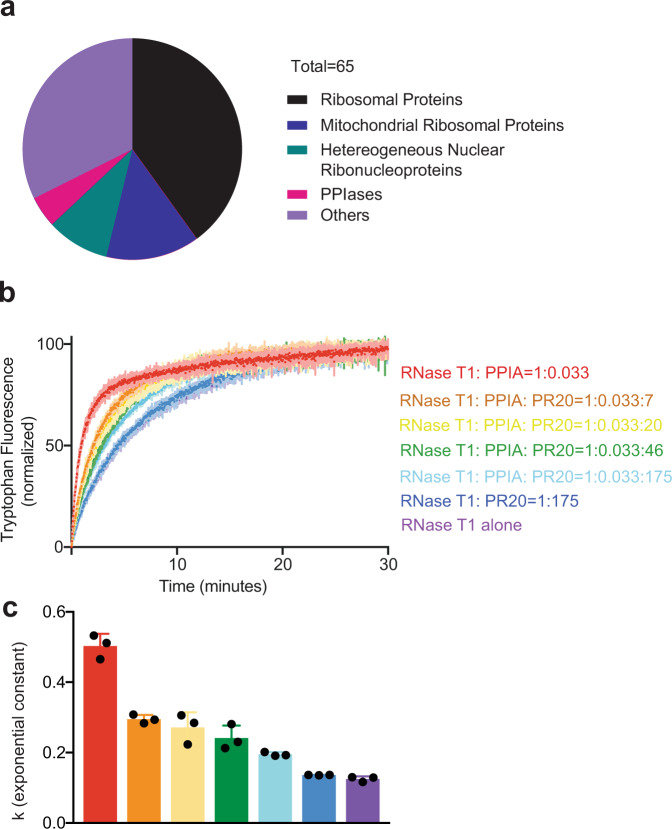
Fig. 1. C9orf72-associated PR repeat polymers inhibit prolyl isomerase folding activity.
a Classification of 65 PR polymer-specific-binding proteins. The data for the analysis were taken from the list of dipeptide repeat polymer interactors identified by Lee et. al. (Table S1 in ref. 5). Only those interactions with a saint score48 more than 0.9 were included. b Inhibition by the 20-dipeptide polymer PR20 of the catalytic effect of PPIA on protein folding of RNaseT1. The increase in fluorescence at 320 nm is shown as a function of the time of refolding in the absence of PPIA and PR20 (violet, “RNaseT1 alone”), and in the presence of a fixed concentration of PPIA and increasing concentrations of PR20 (red, orange, yellow, green, and light blue represent 0, 7, 20, 46, and 175 times excess of PR20 with respect to RNaseT1, respectively). The control experiment showing the refolding of RNaseT1 when PPIA is not present but PR20 has been added is also displayed (dark blue). c Histogram shows the mean value of the exponential folding rate constants k of RNaseT1 in the absence and presence of PPIA and increasing PR20 concentrations. Color coding as in b. n = 3 independent experiments were performed. Error bars represent standard deviation from mean value. k values of each independent experiment are shown in black dots for every condition.