Fig. 4. Inhibition and sequestration of prolyl isomerases by C9ORF72 ALS/FTD-associated PR repeat polymers.
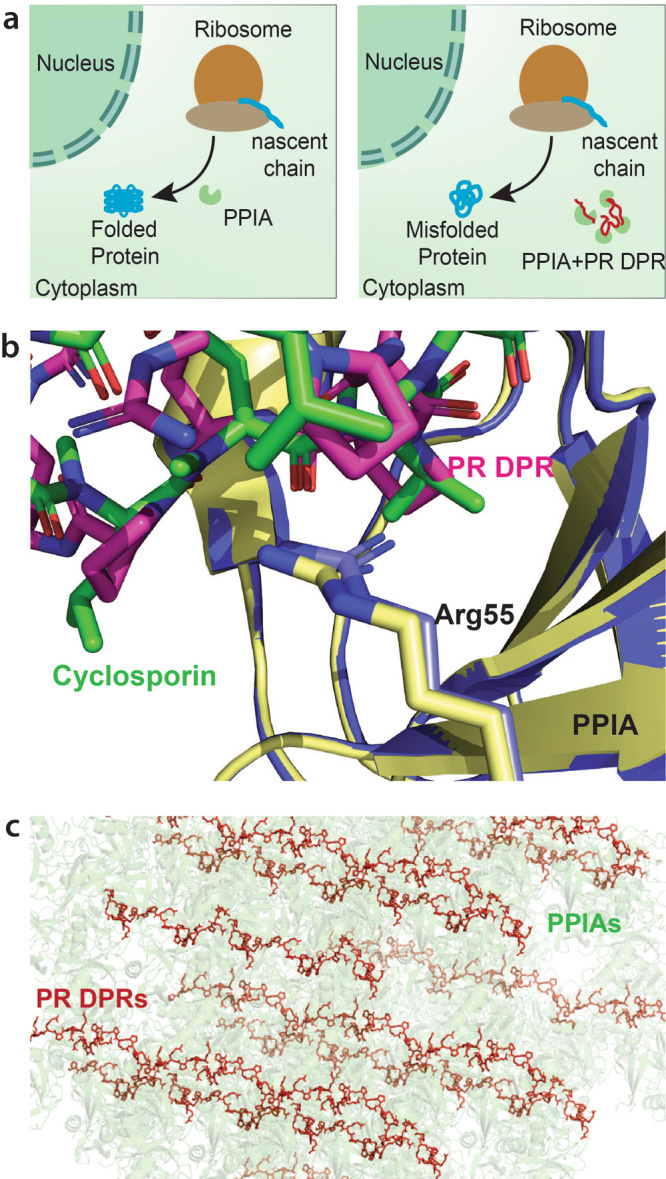
a In normal conditions not associated with disease, prolyl isomerases such as PPIA catalyze the cis–trans isomerization of prolyl peptide bonds and thus help proteins to fold when they exit from the ribosome. PR dipeptide repeat polymers (DPR; red chains) translated from hexanucleotide repeat expansion in the non-coding region of the C9ORF72 gene, bind to the active site of prolyl isomerases and thus block their ability to catalyze protein folding. b Comparison of the active site of the prolyl isomerase PPIA (blue/yellow) in complex with the immunosuppressant drug cyclosporin A (green; PDB code: 1CWA; https://www.wwpdb.org/pdb?id=pdb_00001cwa38) and a PR repeat polymer (pink). c Crystal lattice of the PPIA/PR20 complex illustrating the dense packing of PPIases (green) that is possible on long PR dipeptide repeat polymers (DPR, red).
