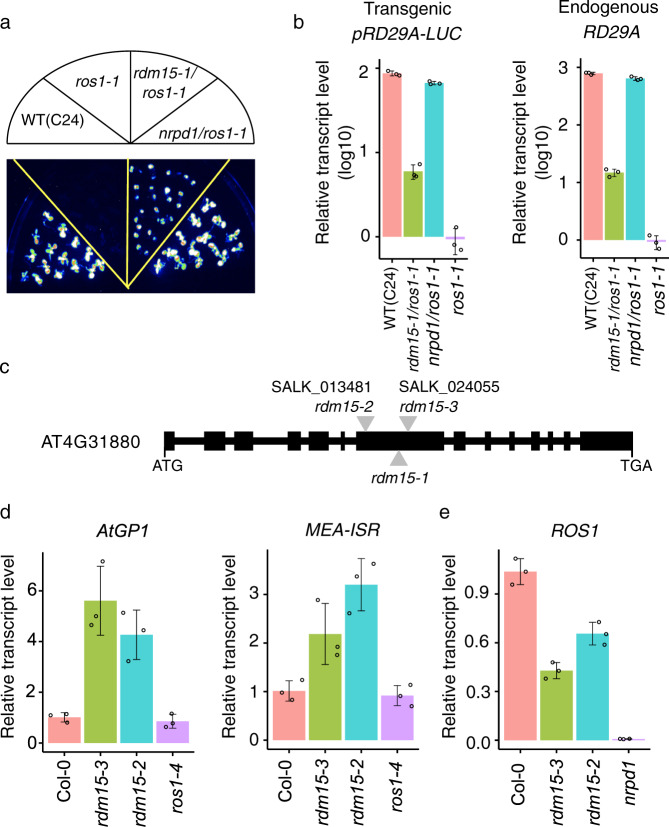
Fig. 1. RDM15 mediates transcriptional silencing.
a Isolation of the rdm15-1 mutant. The wild-type (WT) of the C24 ecotype carries a stress-inducible RD29A-LUC transgene, the expression of which can be assessed by luminescence. The WT, ros1-1, rdm15-1ros1-1, and nrpd1ros1-1 plants were grown for 10 days and imaged after cold treatment (48 h, 4 °C). b RT-qPCR analysis of relative transcript levels of transgenic RD29A-LUC and endogenous RD29A in the WT, rdm15-1 ros1-1, nrpd1 ros1-1, and ros1-1. Ten-day-old seedlings were used for RNA extraction after cold treatment (48 h, 4 °C). c Diagram showing the positions of T-DNA insertions in rdm15-1, rdm15-2, and rdm15-3. Boxes and lines denote exons and introns of RDM15 (AT4G31880), respectively. d RT-qPCR analysis of relative transcript levels of AtGP1 and MEA_ISR in Col−0 (WT), rdm15-2, rdm15-3, and ros1-4. e RT-qPCR analysis of relative transcript level of ROS1 in Col-0, rdm15-2, rdm15-3, and nrpd1-3. ACTIN2 served as the internal control in the RT-qPCR analysis. Error bars represent s.d. (n = 3 biologically independent samples).