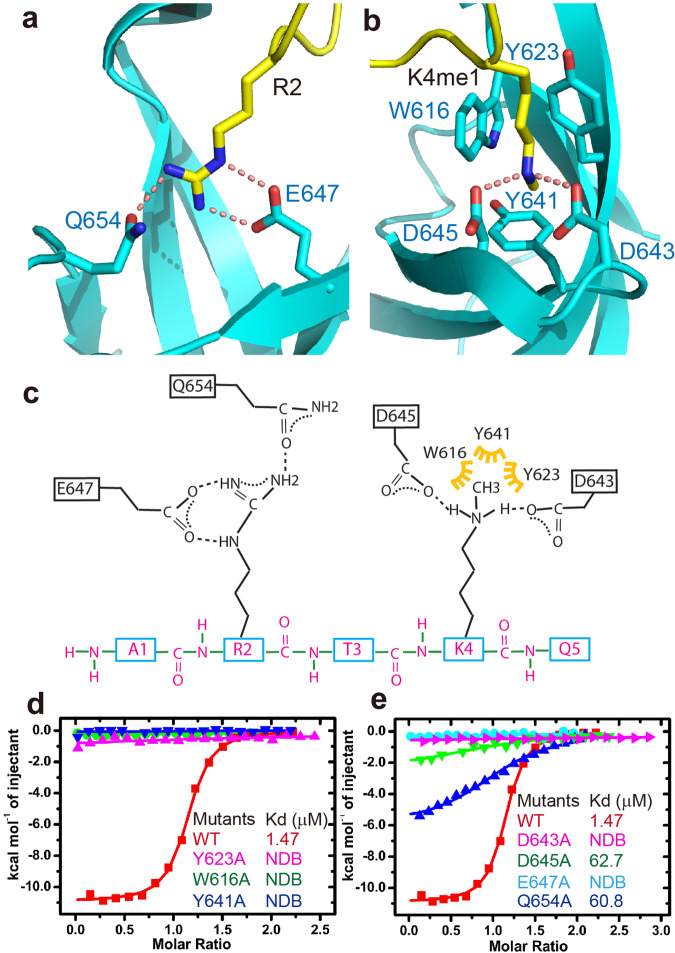
Fig. 6. Details of the specific interaction between the RDM15 Tudor domain and the H3K4me1 peptide.
a The side chain of H3R2 is specifically recognized by Glu647 and Gln654 of the Tudor domain through a salt bridge and hydrogen-bonding interactions. The hydrogen bonds are highlighted with dashed red lines. b The methyl group of H3K4me1 is specifically accommodated within an aromatic cage formed by Trp616, Tyr623, and Tyr641. The two monomethylammonium protons of monomethyllysine form hydrogen bonding and salt bridge interactions with two negatively charged Asp643 and Asp645 residues. c A schematic representation of the intermolecular interactions between RDM15 and the H3K4me1 peptide. d, e The ITC binding curves between the H3K4me1 peptide and the RDM15 Tudor domain mutations showing that the disruption of the aromatic cage (d) or the residues involved in hydrogen bonding interactions (e) dramatically decreases the binding affinity.