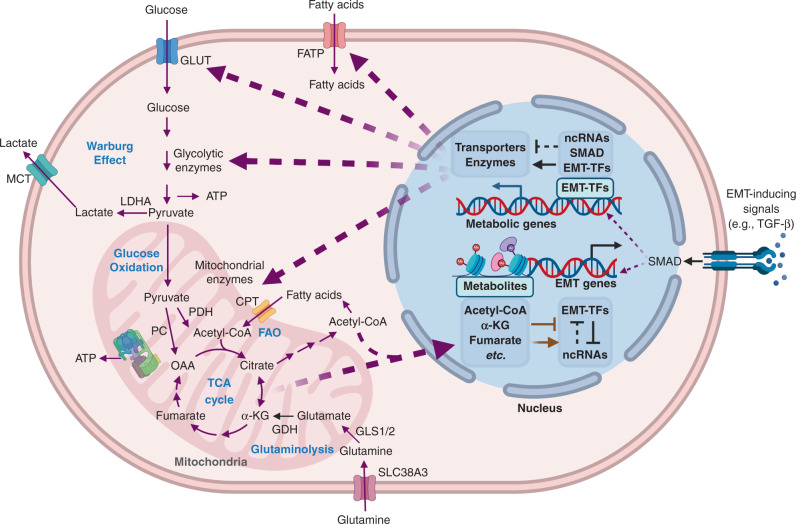
Fig. 1. Crosstalk between EMT and metabolism in cancer.
The purple arrows represent metabolic fluxes. The black arrows/bar-headed arrows represent transcriptional regulation. The black dotted bar-headed arrows represent ncRNA-mediated regulation. The brown arrows/bar-headed arrows represent epigenetic regulations. The purple dotted arrows represent the transportation of molecules that mediate the interaction between EMT and metabolic reprogramming. EMT-inducing signals, EMT-TFs and EMT-associated ncRNAs can directly regulate the transcription or translation of metabolic enzymes and transporters. In turn, the metabolic intermediates can facilitate epigenetic modification of EMT-associated genes or proteins. For example, the EMT-TFs Slug/Twist can repress mitochondrial respiration via suppression of SDH. SDH suppression leads to accumulation of succinate. Succinate accumulation can cause DNA hypermethylation by inhibiting TET2, and subsequently promotes EMT. More details about the EMT-metabolism crosstalk can be found in sections “how does EMT affect metabolism?” and “how does cancer metabolism affect EMT”. GLUT glucose transporter, FATP fatty acid transporter protein, MCT monocarboxylate transporter, LDHA lactate dehydrogenase A, PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase, PC pyruvate carboxylase, OAA oxaloacetic acid, α-KG α-ketoglutarate, CPT carnitine palmitoyltransferase, GDH glutamate dehydrogenase, GLS glutaminase, ncRNA non-coding RNA, EMT-TF EMT-inducing transcription factor. The Figure was created by BioRender.com.