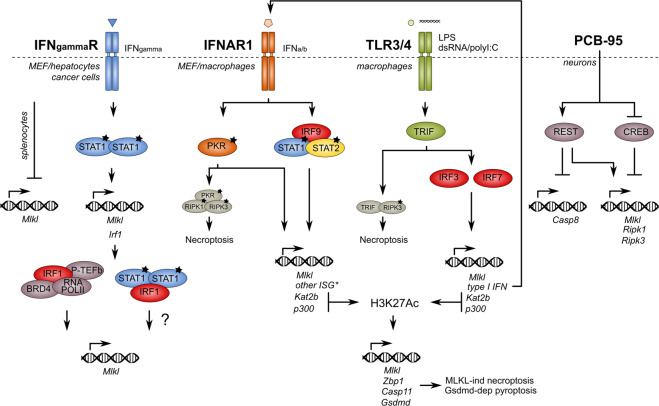
Fig. 5. Transcriptional regulation of MLKL/Mlkl.
IFN signaling induces transcription of MLKL by different mechanisms, including direct binding of STAT1 to the promoter of MLKL and IRF-regulated expression of acetyltransferases that can activate transcription of MLKL by acetylation of its promoter. Also CREB can directly bind to the MLKL promoter, thereby repressing MLKL expression. Finally, REST can (in)directly activate MLKL transcription. * = another interferon-stimulated gene that might be involved in necroptosis signaling. Irf1/3/7/9 interferon regulatory factor 1/3/7/9, Gsdmd gasdermin D, Casp 8/11 caspase-8/11, Zbp1 Z-DNA binding protein 1, STAT1/2 signal transducer and activator of transcription 1/2, PKR protein kinase R, ISG interferon-stimulated gene, H3K27Ac histon 3 lysin 27 acetylation, p300 histone acetyltransferase p300, Kat2b lysine acetyltransferase 2b, TRIF TIR-domain-containing adaptor-protein inducing IFN-β, PCB-95 polychlorinated biphenyl-95, LPS lipopolysaccharide, IFNgammaR interferon gamma receptor, IFNAR1 interferon alpha receptor, TLR3/4 toll-like receptor 3/4, REST RE1-silencing transcription factor, CREB cAMP responsive element binding protein, BRD4 bromodomain 4 protein, RNA-POLII RNA polymerase II, P-TEFb positive transcription elongation factor.