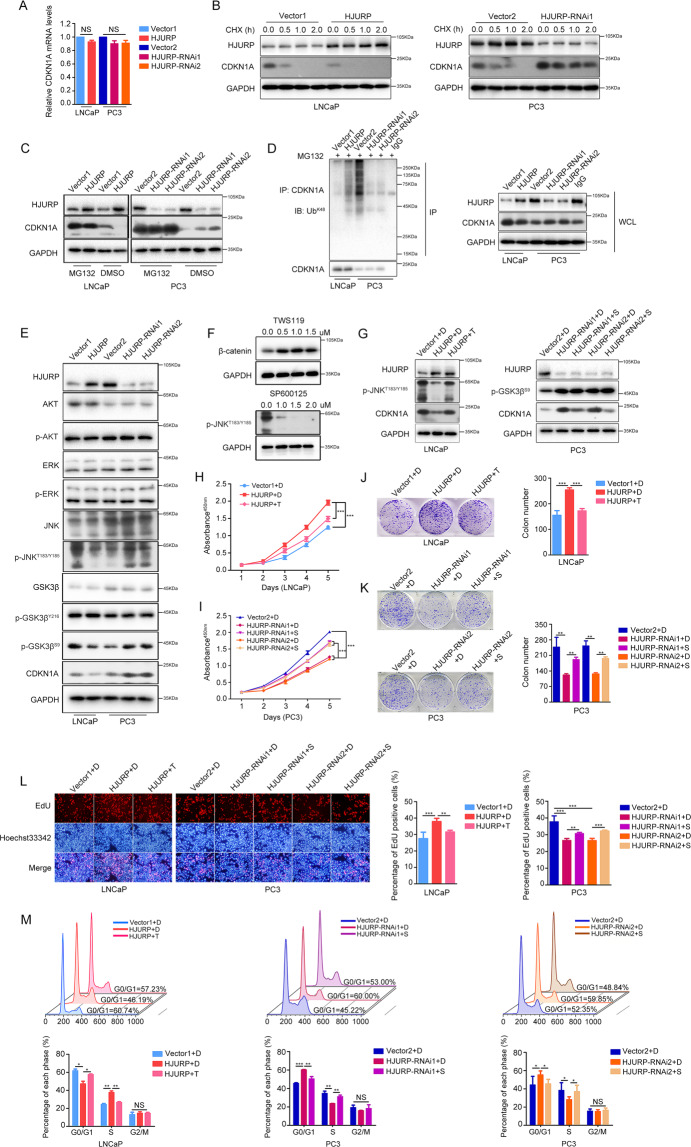
Fig. 5. HJURP promotes CDKN1A ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation through the GSK3β/JNK pathway.
A qPCR quantification of CDKN1A mRNA levels in PCa cells after HJURP-overexpression or -silencing. B CHX (50 µg/mL) was used to treat LNCaP and PC3 cells for 0, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 h, and western blotting was applied to quantify CDKN1A stability. C MG132 (10 µM) was employed to incubate cells for 6 h, and western blotting was utilized to quantify CDKN1A levels after HJURP -overexpression or -knockdown in PCa cells. D CO-IP quantification of the effects of HJURP on CDKN1A ubiquitination. E Western blotting of AKT, p-AKT, ERK1/2, p-ERK1/2, JNK, p-JNKT183/Y185, GSK3β, p-GSK3βY216, p-GSK3βS9, and CDKN1A levels in PCa cells after HJURP-overexpression or -silencing. F Western blotting quantified optimal TWS119 and SP600125 concentrations (0.5 µM TWS119 and 1.0 µM SP600125 were selected). G TWS119 could reverse HJURP-induced reduction in p-JNKT183/Y185 and CDKN1A, whereas SP600125 could reverse HJURP-induced CDKN1A elevation, but did not affect p-GSK3βS9 levels. H–M TWS119 and SP600125 could reverse HJURP-induced changes in cell viability (H), clonogenic potential (J), proliferative capacity (L), and cell cycle (M) in PCa cells. CHX cycloheximide, DMSO dimethyl sulfoxide, Ub ubiquitination.