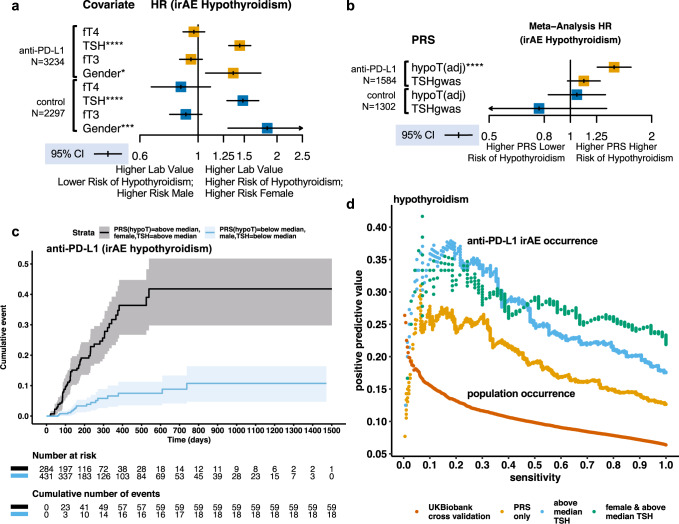
Fig. 3. Genetic variation associated with lifetime risk of thyroid autoimmunity affects hypothyroidism irAE risk during atezolizumab treatment and acts independently of pre-treatment risk factors.
a IPD meta-analysis assessing the association between hypothyroidism irAE and potential pre-treatment risk factors in a multivariable mixed effects Cox model fit to data from (N = 3234) atezolizumab and (N = 2297) standard of care treated cancer patients in the safety evaluable population with pre-treatment thyroid hormone measurements across the 7 clinical trials analyzed stratified across arms. Measurements were normalized across patients by normalization to the quantiles of a standard normal distribution and modeled as random effects. Point estimates and 95% CI for HR for hypothyroidism expressed in unit normalized hormone levels after fitting the model. TSH = pre-treatment measured thyroid-stimulating hormone; fT4 = free thyroxine; fT3 = free triiodothyronine. Gender is encoded as 1 = female and 0 = male. p-values for a two-sided Wald test that the log-HR is non-zero for fT4 p = 0.44, TSH p = 9.93 × 10−14, and gender p = 0.012 in atezolizumab treated patients and fT4 p = 0.25, TSH p = 3.26 × 10−8, and gender p = 0.00054 in standard of care treated patients. b Random effect point estimate and 95% CI for the IPD meta-analysis hazard ratio expressed in normalized unit PRS for the time to occurrence of hyperthyroidism irAE estimated using a mixed effect Cox model with genotype eigenvectors as fixed effect covariates in (N = 1584) atezolizumab and (N = 1302) standard of care treated European ancestry cancer patients across 7 clinical trials. TSHgwas uses a PRS constructed from a GWAS of TSH levels in individuals not receiving any medication for thyroid dysfunction. hypoT(adj) computes the association between a hypothyroidism irAE and the hypothyroidism PRS adjusted for measured pre-treatment TSH levels and gender using these as additional fixed effect covariates in the model. Meta-analysis p-values for a two-sided Wald test that the estimated log-HR is non-zero for hypoT(adj) p = 3.91 × 10−7 and TSHgwas p = 0.11 in atezolizumab treated patients and hypoT(adj) p = 0.66 and TSHgwas p = 0.36 in the standard of care treated patients stratified across trial arms. c Cumulative incidence plot comparing risk of hypothyroidism in atezolizumab patients with and without all of the pre-treatment risk factors identified for hypothyroidism irAE in atezolizumab treated cancer patients. d Positive predictive value and sensitivity (also known as precision and recall) for hypothyroidism irAE and population hypothyroidism occurrence across thresholds for the PRS in atezolizumab treated patients and estimated by 4-fold cross validation in the UK Biobank respectively. Curves were also generated for subgroups that have increasing incidence of hypothyroidism irAE. Meta-analysis: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.