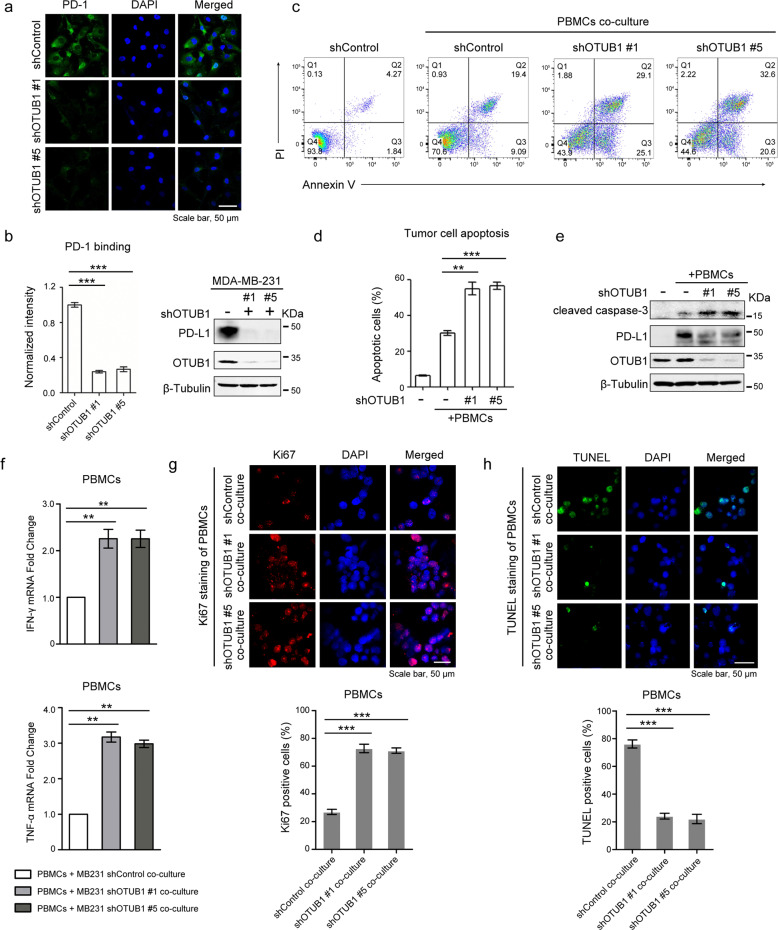
Fig. 5. Depletion of OTUB1 impairs PD-L1 function in T cell-mediated cancer cell killing.
a Immunofluorescence assays to detect PD-1 binding intensity. MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing shControl or shOTUB1 were incubated with recombinant human PD-1 Fc protein and then anti-human Alexa Fluor 488 dye. Scale bar, 50 µm. b Normalized intensity of PD-1 binding and immunoblotting of OTUB1 expression to show knockdown efficiency. c FACS analysis of PBMCs-mediated killing of tumor cells using Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) double staining. Healthy cells are negative for both stains in the Q4 quadrant. The Q3 quadrant shows Annexin V-positive cells, which are in the early stage of apoptosis. The Q2 quadrant shows cells that are both Annexin V- and PI-positive, which are in the late stage of apoptosis. d Quantitative apoptotic measurement of Q2 and Q3 quadrants. Greater than 104 cells were counted for each group. e Immunoblotting of cleaved caspase-3 levels in shControl or shOTUB1 MDA-MB-231 cells after incubation with activated PBMCs. f The qRT-PCR analyses of IFN-γ and TNF-α mRNA expressions in PBMCs after co-culture with MDA-MB-231 shControl or shOTUB1 cells. g, h The Ki67 or TUNEL staining of PBMCs after co-culture with MDA-MB-231 shControl or shOTUB1 cells. The percentage of Ki67 or TUNEL positive staining cells were analyzed using the ImageJ software. The results of b, d, f, g and h are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.