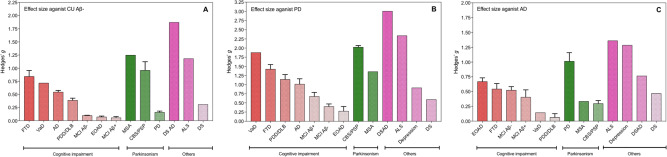
Fig. 2. Effect sizes of neurodegenerative disorders as compared to amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired controls, Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Effect sizes (Hedges’s g) of different neurodegenerative disorders as compared to amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired controls (A n = 403), Parkinson’s disease (B n = 311), and Alzheimer’s disease (C n = 236). The bars represent the mean effect size for the cohort, whereas the error bars represent the standard deviation of effect size when considering the KCL and Lund cohorts separately. Those without error bars (e.g., VaD) are only included in one cohort. AD Alzheimer’s disease (n = 236), ALS amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (n = 50), CU Aβ− cognitively unimpaired without Aβ pathology (n = 403), CBS/PSP corticobasal syndrome and progressive supranuclear palsy (n = 43), depression (n = 37), DS Down syndrome (n = 29), DSAD Down syndrome Alzheimer’s disease (n = 12), EOAD early-onset Alzheimer’s disease (n = 82), FTD frontotemporal dementia (n = 204), MCI Aβ− mild cognitive impairment without Aβ pathology (n = 170), MCI Aβ + mild cognitive impairment with Aβ pathology (n = 196), MSA multiple system atrophy (n = 29), PD Parkinson’s disease (n = 311), PDD/DLB Parkinson’s disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies (n = 105), VaD vascular dementia (n = 22).