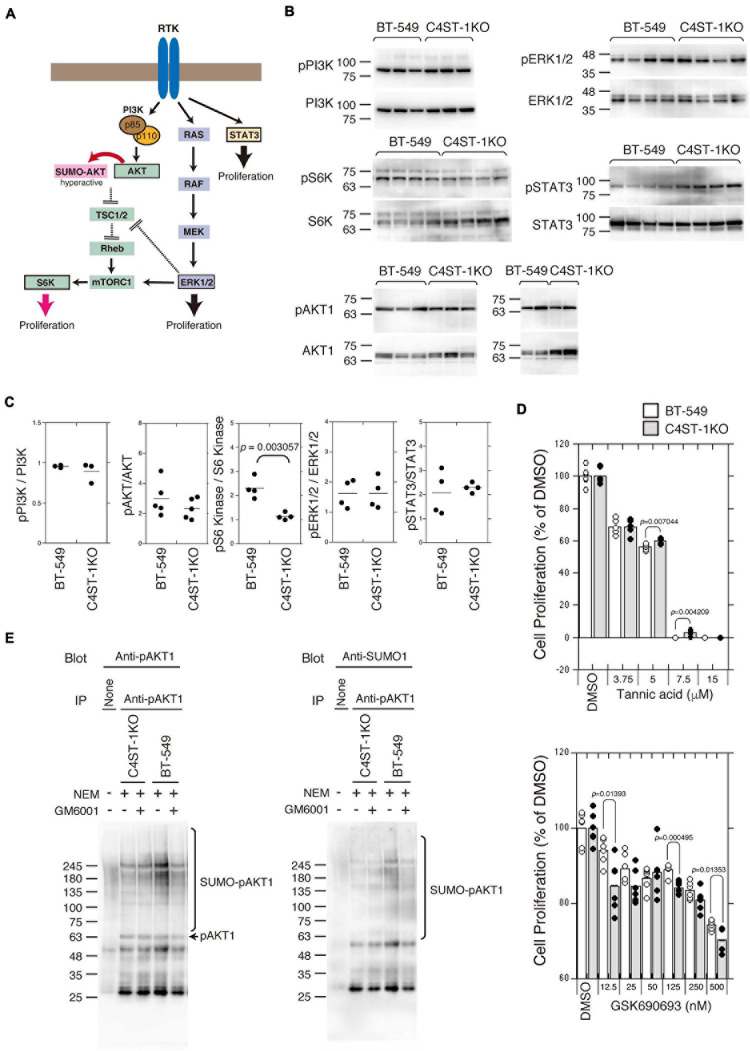
FIGURE 3.
Suppression of SUMOylation of AKT1 by the loss of C4ST-1 expression. (A) Some of the signaling pathways involved in cancer proliferation examined in this study are shown. (B) Phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT1, S6K, ERK1/2, and STAT3 in BT-549 and C4ST-1 KO cells was examined by immunoblotting using phospho-specific antibodies and total antibodies. (C) Phosphorylation of PI3K (n = 3), AKT1 (n = 5), S6K (n = 4), ERK1/2 (n = 4), and STAT3 (n = 4) in BT-549 and C4ST-1 KO cells was quantified by calculating the ratios of phosphorylated to total protein. (D) The effect of tannic acid and AKT inhibitor (GSK690693) on the proliferation of BT-549 and C4ST-1KO cells. (E) SUMOylation of AKT1 in BT-549 and C4ST-1 KO cells were examined. Both the cells were treated with (+) or without (−) GM6001, and lysed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), which inhibits SUMO proteases. Immunoprecipitated phospho-AKT1 proteins were subject to immunoblotting using anti-pAkt1 and anti-SUMO1 antibodies.