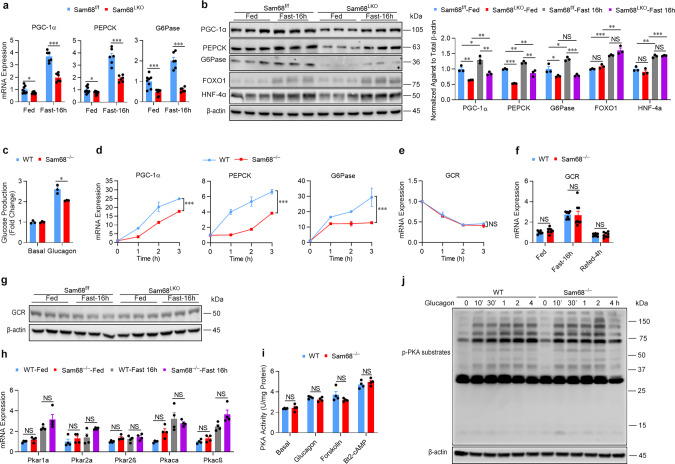
Fig. 2. Hepatic Sam68 deficiency reduces glucagon signaling and gluconeogenic gene expression.
a mRNA and b protein expression of gluconeogenic genes were evaluated via qRT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively, in the livers of Sam68LKO and Sam68f/f mice under feeding conditions and after the animals had been fasted for 16 h (a; Fed, n = 8; Fast-16 h, n = 6. b; n = 3). c Glucose production was measured in WT and Sam68−/− primary hepatocytes that had been cultured with (Glucagon) or without (Basal) glucagon (100 nM) for 4 h (n = 3). d mRNA expression of gluconeogenic genes was measured in WT and Sam68−/− primary hepatocytes after treatment with glucagon for 0−3 h (n = 3). mRNA expression of the glucagon receptor (GCR) was evaluated (e) in WT and Sam68−/− primary hepatocytes after treatment with glucagon for 0−3 h (n = 3) and (f) in the livers of WT and Sam68−/− mice under feeding conditions (WT, n = 6; Sam68−/−, n = 8), after fasting the animals for 16 h (WT, n = 8; Sam68−/−, n = 8), and after 16 h of fasting followed by 4 h of refeeding (WT, n = 8; Sam68−/−, n = 8). g Protein expression of GCR was assessed by Western blotting (n = 3). h mRNA expression of PKA subunits was evaluated in the livers of WT and Sam68−/− mice under feeding conditions or after 16 h of fasting (n = 4). i PKA activity was measured in WT and Sam68−/− primary hepatocytes after treatment with PBS (basal), glucagon, forskolin (10 μM), or Bt2-cAMP (100 μM) for 30 min (n = 4). j WT and Sam68−/− primary hepatocytes were treated with glucagon for 0−30 min and for 1−4 h; then, protein levels of phosphorylated PKA substrates were evaluated. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, NS, not significant (two-way ANOVA). “n” denotes biologically independent primary hepatocyte samples or liver tissues. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.