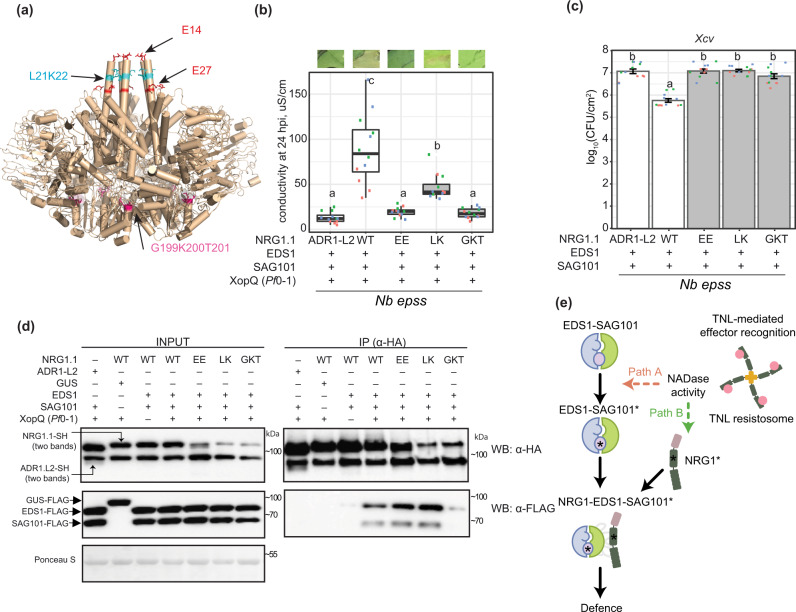
Fig. 6. Association between Arabidopsis NRG1.1, EDS1 and SAG101 require an intact NRG1.1 P-loop.
a A structure homology model of Arabidopsis NRG1.1 based on the ZAR1 resistosome. NRG1.1 amino acids E14 and E27 (red sticks) and L21 and K22 (blue sticks) aligned with residues E11, E18, F9, L10 and L14 in ZAR1. The modelled NRG1.1 P-loop motif (G199 K200 T201) is shown as cyan sticks. XopQ-triggered cell death (b) and Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85-10 (Xcv) growth restriction (c) in Nicotiana benthamiana eds1a pad4 sag101a sag101b (Nb epss) expressing Arabidopsis NRG1.1-SH wildtype, NRG1.1E14A/E27A, NRG1.1L21A/K22A and NRG1.1G199A/K200A/T201A variants together with EDS1-FLAG and SAG101-FLAG. Arabidopsis proteins were expressed via Agrobacteria-mediated transient expression assays two days before infiltration of Pseudomonas fluorescens 0-1 (Pf0-1) XopQ (OD600 = 0.3) or simultaneously with Xcv (OD600 = 0.0005). Experiments were performed three times independently, each with four replicates (leaf discs) (Tukey’s HSD, α = 0.001, n = 12). Error bars represent standard error of mean. Datapoints with the same colour come from one independent experiment. d Immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blot (WB) analyses testing associations of Arabidopsis NRG1.1 mutant variants with EDS1 and SAG101 in Nb epss after triggering Roq1 signalling by Pf0-1 XopQ infiltration (OD600 = 0.3; 10 hpi). Arabidopsis EDS1-FLAG, SAG101-FLAG with NRG1.1-SH, and using GUS-FLAG and Arabidopsis ADR1-L2-SH as negative controls, were expressed using Agrobacteria 2 d prior to Pf0-1 XopQ infiltration. After α-HA IP, the indicated fractions were analysed with α-HA and α-FLAG antibodies by WB. The experiment was conducted three times independently with similar results. e Model of molecular events leading to generation of an Arabidopsis EDS1–SAG101–NRG1 signalling complex essential for TNL receptor-activated defence. NRG1–EDS1–SAG101 association is dependent on TNL activation and requires an intact EDS1–SAG101 heterodimer EP domain cavity (purple circle) and NRG1 nucleotide-binding domain. In two depicted scenarios, an effector-induced TNL oligomer with NADase activity leads to activation (asterisks) of EDS1–SAG101 via the EP domain cavity (‘Path A’, asterisk inside the purple circle) or NRG1 (‘Path B’). These paths are not mutually exclusive. EDS1–SAG101–NRG1 assembly precedes and is necessary for TNL-triggered cell death and resistance involving a predicted NRG1 N-terminal HeLo domain α-helix.