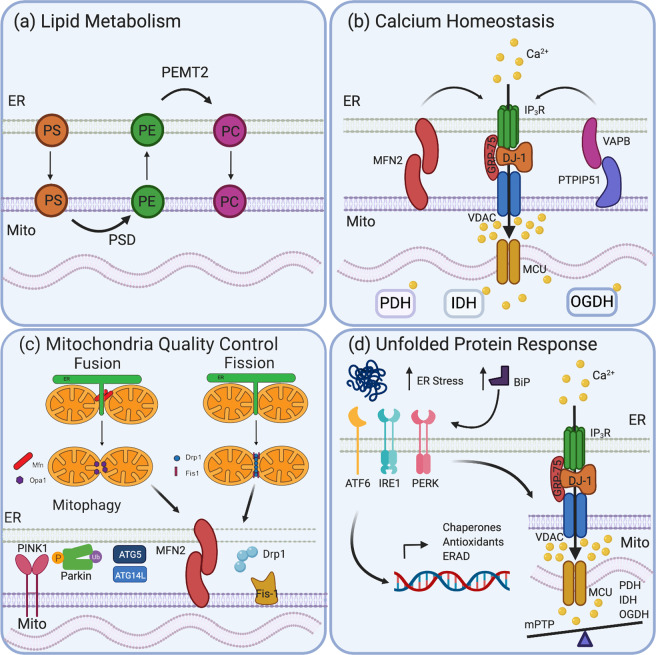
Fig. 2. Cellular functions of mitochondria-ER contact sites.
a Lipid metabolism requires the transfer of phospholipids from the ER to mitochondria and back again at MERCS. Phosphatidylserine (PS) in the ER is transferred to mitochondria where it is converted to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) by enzyme PS Decarboxylase (PSD). PE is shuttled back to ER where PE-N-methyltransferase (PEMT) modifies it to phosphatidylcholine (PC). b Ca2+ homoeostasis underpins many MERCS functions and is essential to maintain cellular health. The tetramer complex IP3R, VDAC, GRP75 and DJ-1 allow transfer of Ca2+ from ER through IP3R and VDAC to the inter mitochondria membrane space, producing Ca2+ hotspots. These hotspots activate MCU, allowing Ca2+ into the mitochondria matrix that promotes enzymes involved in ATP production, such as PHD, IDH and OGDH. c MERCS impacts on MQC pathways. Both mitochondria fission and fusion require the ER and occur at MERCS. Mitochondrial fusion allows the mixing of damaged and healthy mitochondria components, diluting the damage and helping to maintain the overall health of the mitochondria. Mitochondrial fission can protect the mitochondria network by segregating highly damaged sections, promoting mitophagy. Mitochondrial fission genes Drp1 and Fis-1 and mitochondrial fusion genes, MFN1/2 and OPA1 regulate changes in mitochondrial morphology. MFN2 is found in MERCS, and it is established that the ER constricts the mitochondria, allowing oligomerisation of Drp1 around the mitochondria. MERCS is also involved in mitophagy; both PINK1 and Parkin are found in MERCS under mitophagy induction, as well as key autophagy components ATG5 and ATG14L. d The accumulation of unfolded proteins in the ER increases ER stress and upregulates the chaperone protein BIP that initiates the UPR. BiP activates three pathways of the UPR: ATF6, IRE3 and PERK. Activation of these receptors activates chaperone proteins, antioxidant response proteins and ER-associated protein degradation (ERAD) machinery. ER stress can increase Ca2+ import into the mitochondria to increase the efficiency of Ca2+-dependent enzymes PDH, IDH and IGDH required in ATP production, providing energy for the chaperone machinery. A balance is required, however, as high Ca2+ influx into mitochondria, caused by severe ER stress, can trigger mitochondria permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening, leading to mitochondrial swelling and the initiation of apoptosis.