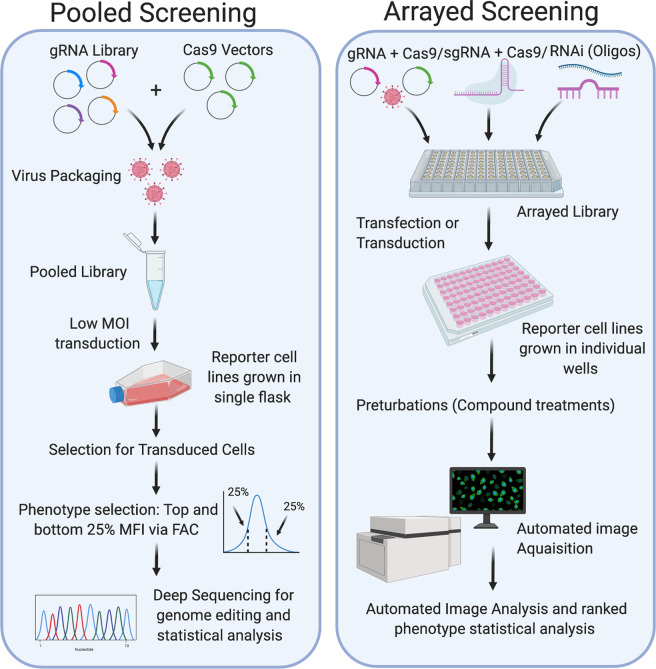
Fig. 5. Workflow for pooled and arrayed screening approaches.
Pooled screening requires the gRNA library and Cas9 to be delivered into cells within a single vessel (using a low MOI viral transduction to maintain a 1:1 ratio of gRNA to cells). The cells then undergo selection for transduced cells and further selection for the phenotype of interest. For example, mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) where the top and bottom 25% are examined for survival. The output for a pooled screen comes from deep sequencing of the genomic DNA from control vs treated samples. Statistical analysis of gRNAs that are enriched or depleted is conducted. Arrayed screens can be conducted with a wider range of silencing techniques, including CRISPR/Cas9 or RNAi. This is because the final readout comes from phenotypic analysis, rather than deep sequencing of genomic DNA. Individual gRNAs and siRNAs are delivered (by transduction or transfection) to cells in specific wells of a 96-well plate (eliminating the possibility that more than one gRNA or si9RNA could be delivered per cell). The transfected cells remain in an arrayed format for phenotype analysis, and statistical analysis in which phenotypes of interest can be matched with gRNA/siRNA by their position in the plate.