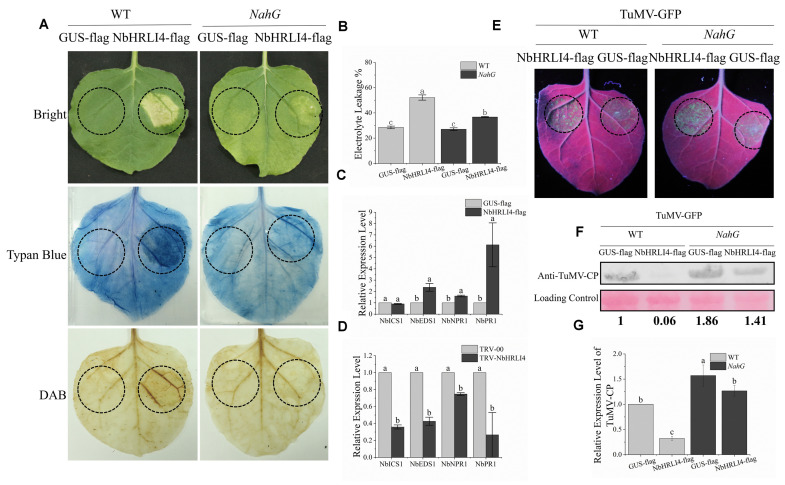
FIGURE 5.
NbHRIL4 induced HR-like cell death in an SA-dependent manner. (A) Overexpression of NbHRLI4 (but not GUS) induced cell death (confirmed by trypan blue staining) at 6 dpi. H2O2 accumulated significantly in areas expressing NbHRLI4 as shown by DAB staining. Overexpression of NbHRLI4 induced less cell death at 6 dpi on NahG plants. (B) NbHRLI4-flag and GUS-flag were overexpressed in both WT and NahG plants. Leaf disks were excised and assayed for electrolyte leakage at 6 dpi. (C) Results of RT-qPCR showing the expression levels of NbEDS1, NbICS1, NbNPR1, and NbPR1 in WT plants overexpressing NbHRLI4-flag or GUS-flag at 3 dpi. (D) Results of RT-qPCR showing the expression levels of NbEDS1, NbICS1, NbNPR1, and NbPR1 in WT plants infected with TRV-HRLI4 or TRV-00 at 12 dpi. T-test was used for mean expression values of single gene between two samples in panel (C) and panel (D). Different letters on histograms indicate significant differences (P < 0.05). (E) Leaves of WT and NahG plants inoculated with TuMV-GFP and overexpressing NbHRLI4-flag or GUS-flag observed under UV light at 4 dpi. (F) Western blotting detection of TuMV-CP on leaves shown in panel (E). (G) Results of RT-qPCR to detect TuMV mRNA in leaves shown in panel (E). The mean expression values in panels (B) and (G) were analyzed using F-test. Different letters on histograms indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).