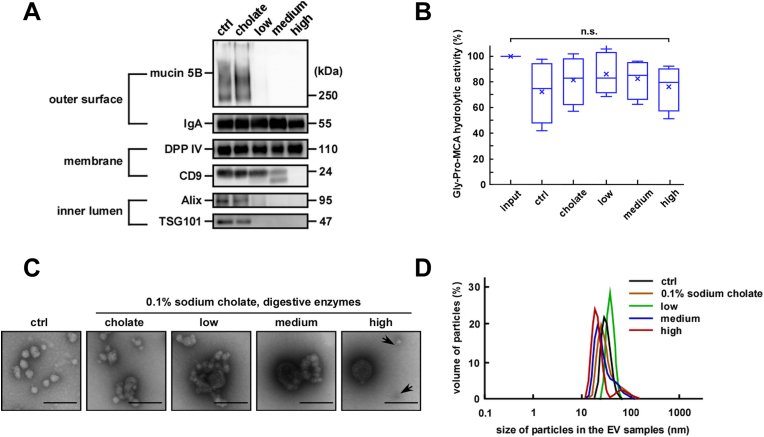
Fig. 5.
Stability of salivary extracellular vesicles (EVs) after sequential treatment. After pepsin treatment under acidic conditions (0.03–3.0 mg/mL, pH 3.0, 37 °C for 3 h) the pH was neutralized. Then sodium cholate (0.1%) and pancreatin (0.01–1 mg/mL) were added to the EV fractions and the mixtures were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. The different combinations of enzyme concentrations used were low (0.03 mg/mL pepsin and 0.01 mg/mL pancreatin), medium (0.3 mg/mL pepsin and 0.1 mg/mL pancreatin) and high (3.0 mg/mL pepsin and 1.0 mg/mL pancreatin). (A) Western blot analysis of the proteins located on the outer surface (mucin 5B and IgA), membrane (DPP IV and CD9), and inner lumen (Alix and TSG101) of salivary EVs (donor A). Two micrograms of proteins from each treated EV fraction were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred onto PVDF membranes, and immunoblotted with antibodies. (B) Changes in the DPP IV activity in the salivary EV fractions. The DPP IV activity in fresh or treated EV fractions was measured in triplicates and is represented as box plots of five independent experiments. The mean is denoted as x. n. s., not significant. The mean is denoted as x. Input indicates fresh and untreated EV fractions, and control (ctrl) indicates EV fractions only subjected to changes in the pH (from pH 3 to pH 7). (C) Morphological analyses of the salivary EV fractions visualized under an electron microscopy (donor A). Black arrows highlight smaller EVs. Scale bar, 100 nm. The morphology of EVs from other donors is shown in Fig. A.6B. (D) Particle size of salivary EVs. The particle size was analyzed using the DLS measurements conducted in triplicates. A typical result is shown (donor A).