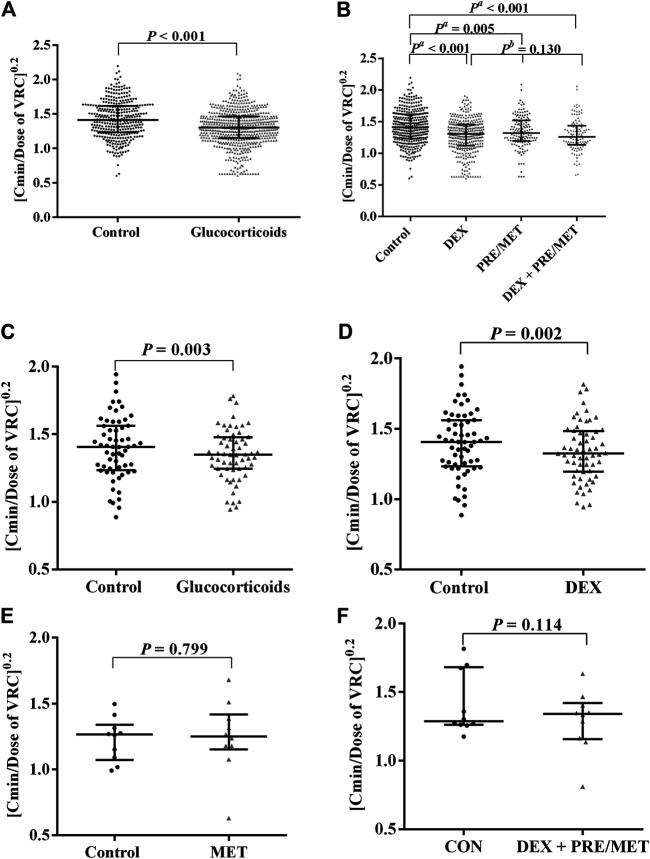
FIGURE 1.
Effects of concomitant glucocorticoids administration on the C/D ratio of VRC. The data were non-normal distribution and expressed as median with interquartile range. The ordinate (C/D ratio of VRC) was processed to the power of 0.2. DEX was abbreviation of dexamethasone, PRE was abbreviation of prednisone or prednisolone, and MET was abbreviation of methylprednisolone. N represented the number of patients enrolled and n represented the number of VRC concentrations in the group. (A) showed that the C/D ratio of VRC was significantly higher in the control patients (n = 348) than the patients receiving glucocorticoids therapy simultaneously (n = 570) (p < 0.001). (B) showed the C/D ratio of VRC in the patients accompanying different kinds of glucocorticoids compared with the control patients (n = 348). Coadministration with DEX (n = 334, p < 0.001), PRE/MET (n = 134, p = 0.005), and DEX + PRE/MET (n = 102, p < 0.001) could all reduce the C/D ratio of VRC significantly, but there was no statistical difference among these three groups (p b = 0.130) (Supplemental Table S1). (C) showed that the C/D ratio of VRC was significantly higher in the control patients (n = 197) than the patients receiving glucocorticoids therapy simultaneously (n = 310) (N = 60, p = 0.003). (D) showed that the C/D ratio of VRC in the patients taking DEX (n = 236) was significantly lower than the control patients (n = 197) (N = 60, p = 0.002). (E) showed that the C/D ratio of VRC in the patients taking MET (n = 31) had no statistical difference compared with the control patients (n = 51) (N = 10, p = 0.799). (F) showed that the C/D ratio of VRC in the patients taking DEX + PRE/MET (n = 35) had no statistical difference compared with the control patients (n = 37) (N = 10, p = 0.114) (Supplemental Table S2).