Figure 1.
Ectopic expression of pro-microglial factors in hiPSCs induces expression of various microglial markers
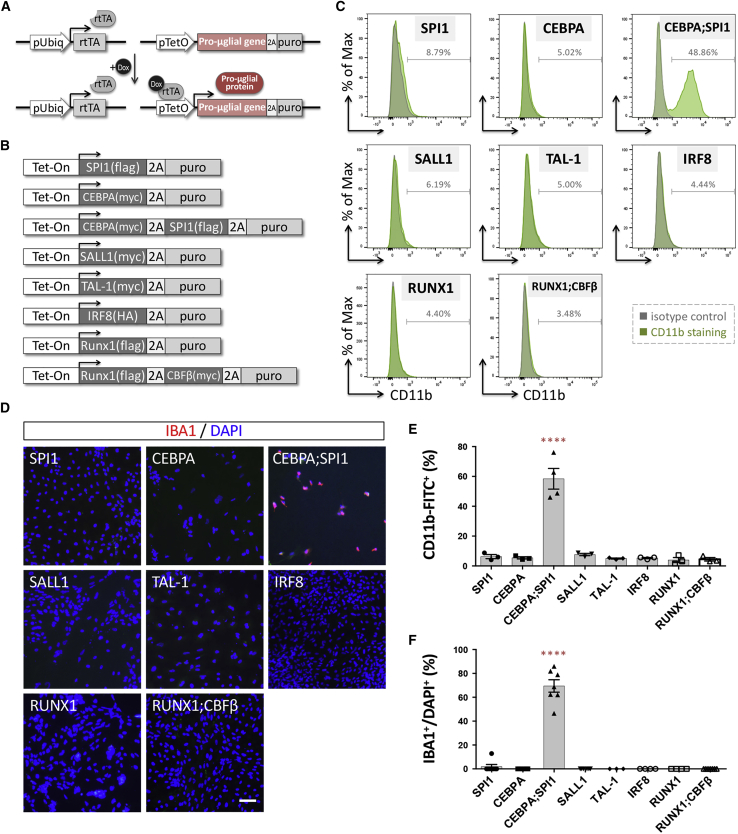
(A) The lentiviral vectors used for pro-microglial (pro-μglial) gene-mediated conversion of hiPSCs to microglia. hiPSCs were sequentially transduced with lentivirus expressing rtTA and then a Tet-On promoter-driven pro-microglial gene linked to puromycin resistance by T2A.
(B) Eight candidate transcription factor constructs involved in defining microglial cell fate during embryogenesis from the literature.
(C) Flow cytometry analysis shows CD11b expression in N2-iPS cells (iN2) ectopically expressing the candidate genes. Green, CD11b antibody conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC); gray, isotype control. The figure is representative of three independent experiments.
(D) Analysis of IBA1 immunoreactivity (red) of iN2 cells ectopically expressing the candidate genes. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(E) Quantification of CD11b+ cells present among iN2 cells ectopically expressing the candidate genes. Data are presented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM; n = 3–4 batches of independent differentiation). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test.
(F) Quantification of the IBA1+ cells present among hiPSCs ectopically expressing the candidate genes. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3–7 batches of independent differentiation). ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test.