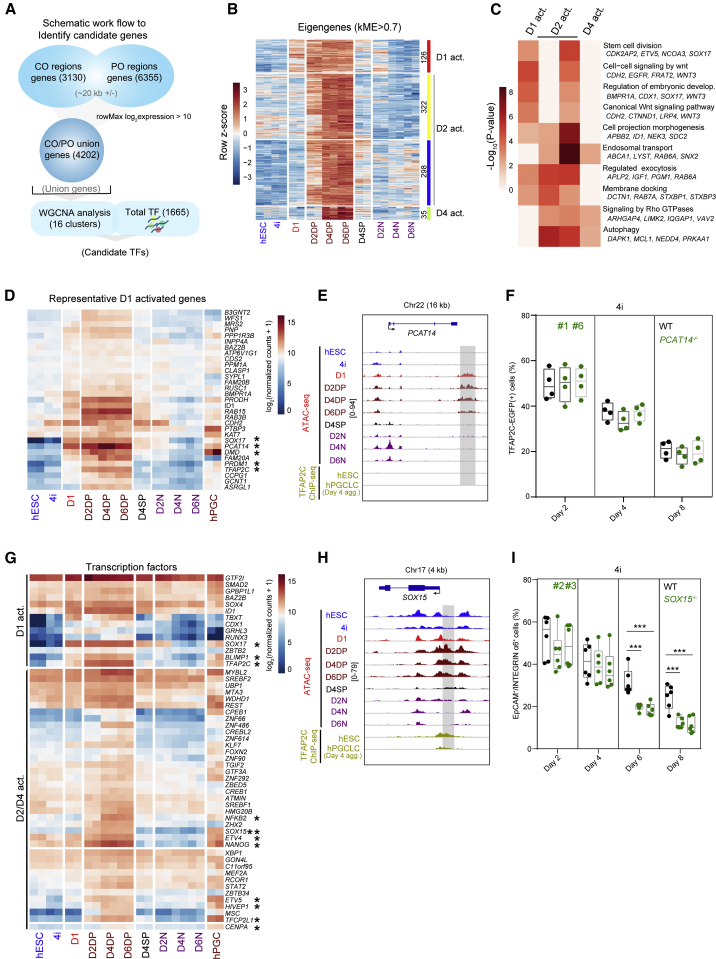
Figure 3.
Transcriptional determinants during the induction of hPGCLCs from hESCs
(A) Schematic representation of candidate genes identification.
(B) Heatmap showing the expression of selected modules in which genes are specifically expressed in DP cells. Module eigengenes score (kME score > 0.7) was used to set the threshold to obtain candidate genes. The red, yellow/blue, and green modules were assigned to day 1-activated (D1 act.), day 2-activated (D2 act.), and day 4-activated (D4 act.) groups.
(C) Gene ontology (GO) analysis of the genes in the D1 act., D2 act., and D4 act. groups as defined in (B).
(D) Heatmap showing the expression pattern of representative D1 act. genes.
(E) Selected genomic views showing the ATAC-seq signals and TFAP2C chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP) signals (Chen et al., 2019) for PCAT14 in the indicated samples. The specific open regions from day 1 are marked with a gray box.
(F) The percentages of TFAP2C-EGFP(+) cells of floating embryoids of WT (black) and PCAT14 knockout (KO) lines (green) upon hPGCLC induction at the indicated days via the 4i method. Results of four independent experiments were shown (n = 4).
(G) Heatmap showing the overall expression of all TFs from the D1/D2/D4 act. modules. Key genes with relatively high expression in hPGCLCs and hPGCs are highlighted.
(H) Selected genomic views showing the ATAC-seq signals and TFAP2C ChIP signals (Chen et al., 2019) for SOX15 in the indicated samples. The specific open regions with TFAP2C binding are marked with a gray box.
(I) The percentages of EpCAM+/INTEGRINα6+ cells of floating embryoids from WT (black) and SOX15 KO lines (green) upon hPGCLC induction at the indicated days via the 4i method. Results of six independent experiments were shown (n = 6). Two-tailed Student's t test was performed, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.