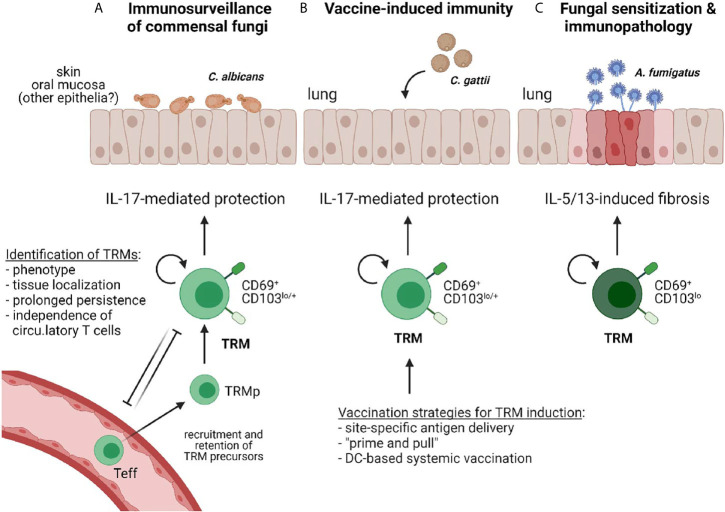
Figure 1.
Reported examples of TRMs in antifungal immunity. (A) IL-17 producing CD4+ TRMs provide immunosurveillance against commensal fungi (e.g. C. albicans) that colonize barrier tissues such as the skin or the oral mucosa to prevent dysbiosis (23, 24). (B) Vaccine-induced immunity protects against fungal pathogens (e.g. C. gattii) via elicitation of IL-17-producing CD4+ TRMs (25). Different vaccination strategies for TRM induction in barrier tissues are indicated. (C) Antifungal TRMs can promote inflammation and immunopathology, such as those induced by A. fumigatus sensitization in the airways (26).