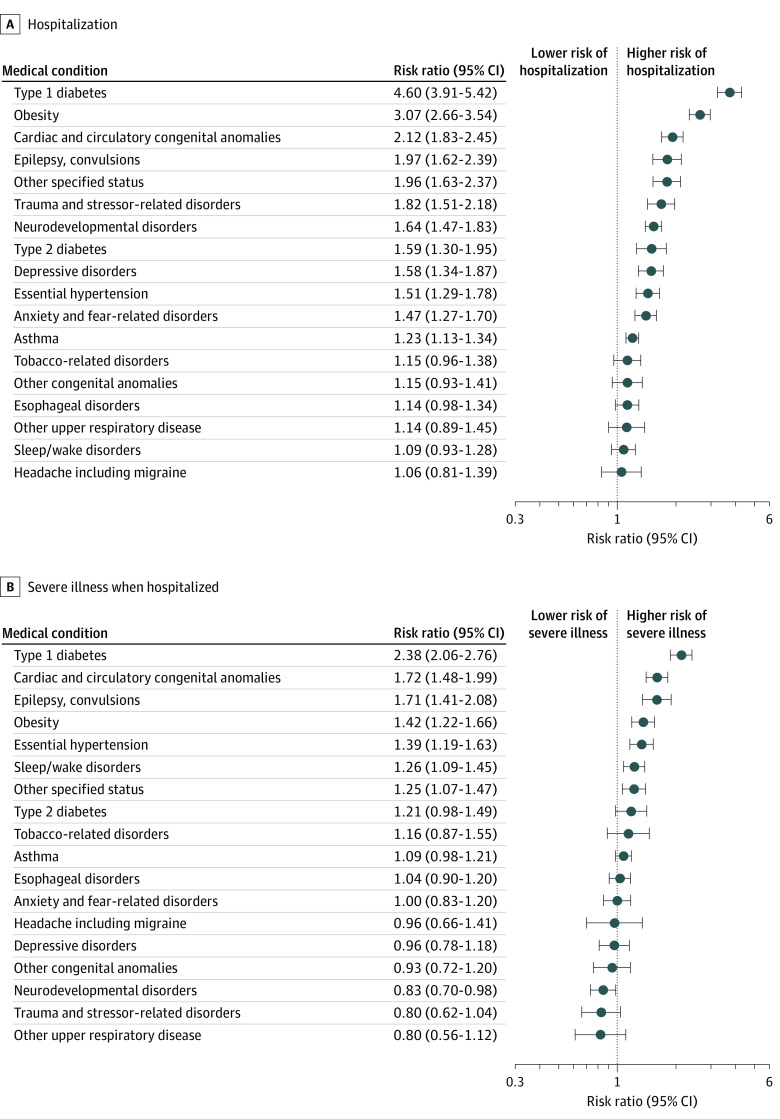
Figure 1. Association Between Underlying Medical Conditions and Risk of Hospitalization or Severe Illness When Hospitalized in the Sample.
Underlying medical conditions were defined as described n the Methods section. The sample was defined as children aged 18 years or younger with a COVID-19 diagnosis during an emergency department or inpatient encounter in hospitals that reported both emergency department and inpatient encounters to Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release, March 2020 through January 2021. Each panel represents results of a single generalized linear model with Poisson distribution and log link function, that includes the following covariates: frequent (ie, prevalence >0.7%) underlying medical conditions, age group, sex, race/ethnicity, payer type, hospital urbanicity, hospital US Census region, admission month, and admission month squared. The reference group for each underlying condition was absence of that condition; the reference group for type 1 and type 2 diabetes was no diabetes.