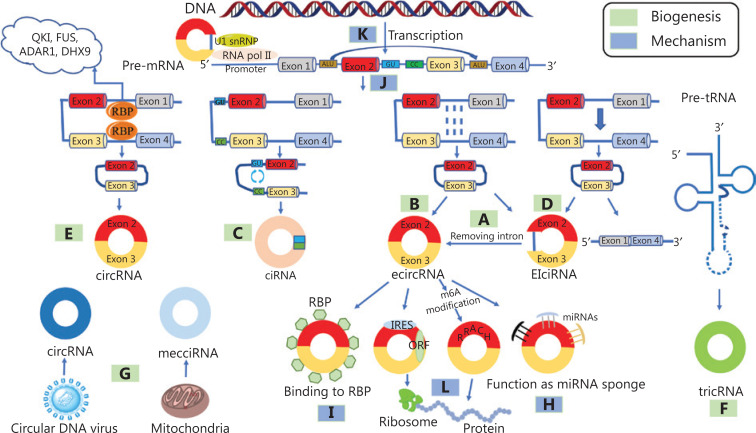
Figure 1.
Biogenesis of circRNAs and the mechanisms of action of circRNAs. (A) Lariat-driven circularization (ecircRNA). (B) Intron-pairing-driven circularization (ecircRNA). (C) Circular intronic RNA. (D) Exon-intron-derived circRNA (EIciRNA). (E) RNA-binding protein (RBP)-driven circularization-derived circRNA. (F) The tRNA precursor-derived. (G) Other sources: fusion gene, circular DNA tumor virus, mitochondrial DNA-originated and mitochondria-encoded circular RNA (mecciRNA). (H) Functioning as miRNA sponges. (I) Interactions with RNA-binding proteins. (J) Involvement in alternative splicing regulation. (K) Regulation of parental gene transcription. (L) Protein-coding potential. QKI, Quaking; FUS, fused in sarcoma; ADAR1, adenosine to inosine acting on RNA enzyme 1; DHX9, DEAH-box helicase 9. IRES, internal ribosome entry site; ORF, open reading frame.