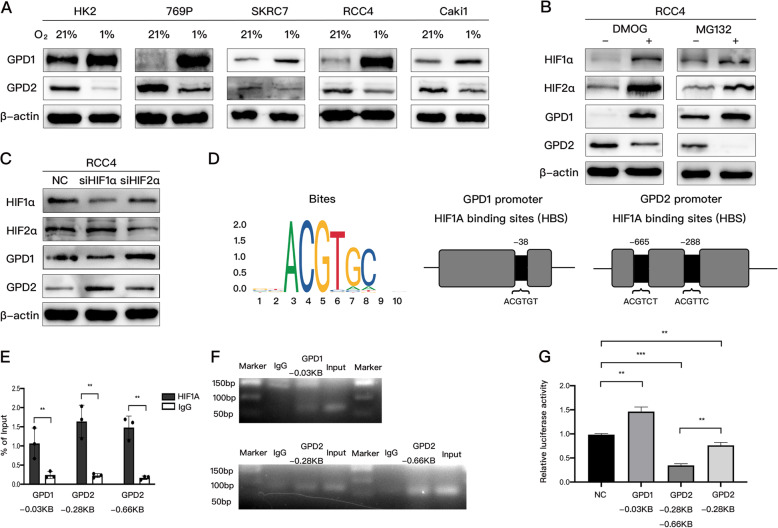
Fig. 4.
HIF1α directly targeted and positively regulated GPD1 and negatively regulated GPD2 at the transcriptional level. (A) HK2, 769P, SKRC7, RCC4, and Caki1 cells were exposed to 21% O2 or 1% O2 for 24 h, followed by examining GPD1 and GPD2 protein expression. (B) RCC4 cells were treated with DMOG (1 mmol/L) or MG132 (10 μmol/L) for 24 h, followed by western blotting. (C) RCC4 cells were transfected with HIF1α-specific siRNA (siHIF1α) or HIF2α-specific siRNA (siHIF2α) or negative control siRNA, followed by western blotting for indicated proteins. (D) Analysis of HIF1α binding sites (HBS) in human GPD1 and GPD2 promoters based on the JASPAR promoter database. (E) A CUT&RUN assay and qRT-PCR were performed with primers containing putative HBS sites in the GPD1 or GPD2 promoters. (F) GPD1 or GPD2 DNA were quantified using DNA agarose gel electrophoresis and qRT-PCR with different primers. (G) A luciferase reporter assay was performed in HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated promoter plasmids, including GPD1-HBS (− 38 bp), GPD2-HBS1 (− 665 bp), and GPD2-HBS2 (− 288 bp). Data are shown as the mean + SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired Student’s t test with a two-tailed distribution (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Abbreviations: HIF, hypoxia inducible factor; GPD1, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1; GPD2, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2; DMOG, dimethyloxalylglycine