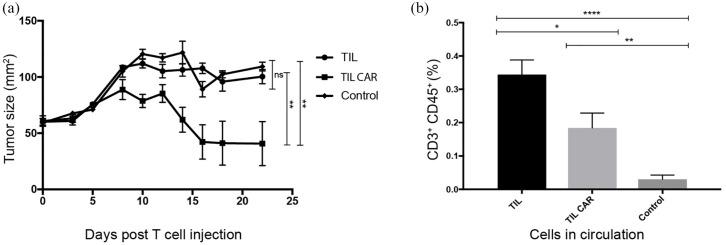
Figure 8.
ACT using TIL transduced with anti-Her2 CAR inhibited tumor growth in mice.
(a) ACT using 1 × 107 TILs transduced with anti-Her2 CAR or non-transduced TILs was delivered into NSG mice bearing established (>50 mm2) xenografts of an autologous patient melanoma tumor cell line. A control (untreated group) was included for comparison. Time is measured from the day ACT was performed (day 0). Treated mice also received five intraperitoneal injections of IL-2 (50,000 IU/injection per mouse) over 3 days. Tumor growth was significantly inhibited by ACT using CAR-transduced T cells. Results are from a single experiment, with seven mice per treatment group and nine mice for control group. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t-test. (b) A greater proportion of non-transduced TILs was detected in the peripheral circulation following ACT. A peripheral blood sample was drawn from each of the mice on day 3 (n = 7–9) following delivery of ACT and analyzed for human T cells using flow cytometry. Mice received TILs (parental) or TILs transduced with anti-Her2 CAR. Significantly greater numbers of circulating TILs were detected in the peripheral circulation of mice following intravenous injection compared with controls. Cells were gated on morphology, viability, CD3+ and CD45+.
Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t-test (*p ⩽ 0.05, **p ⩽ 0.01, ****p ⩽ 0.0001, ns: not significant).
ACT, adoptive cell therapy; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; TIL, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte.