Figure 2.
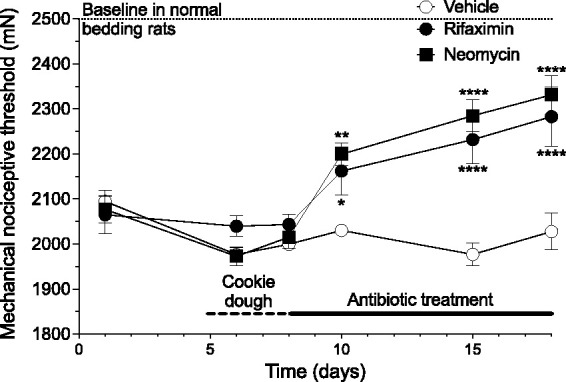
Antibiotics, rifaximin and neomycin, attenuate NLB-induced muscle mechanical hyperalgesia. Adult NLB rats were fed 4 g cookie dough (vehicle), or cookie dough containing rifaximin (50 mg/kg in 4 g cookie dough) or neomycin sulfate (50 mg/kg in 4 g cookie dough). The muscle mechanical nociceptive threshold of NLB rats was lower (i.e., they were hyperalgesic) compared to rats raised on standard bedding (threshold indicated by dashed lines) prior to antibiotic feeding. While rats receiving vehicle (cookie dough) showed no change in nociceptive threshold, both antibiotics significantly increased nociceptive threshold (2-way ANOVA, Time x Antibiotic treatment interaction F16,171 = 5.78, P < 0.0001). Dunnett’s multiple comparison test showed significant differences for both antibiotics from vehicle control rats on days 10 – 22, *P,0.05, **P < - 0.005, ****P < 0.0001); Control n = 6, both rifaximin and neomycin n = 10.
