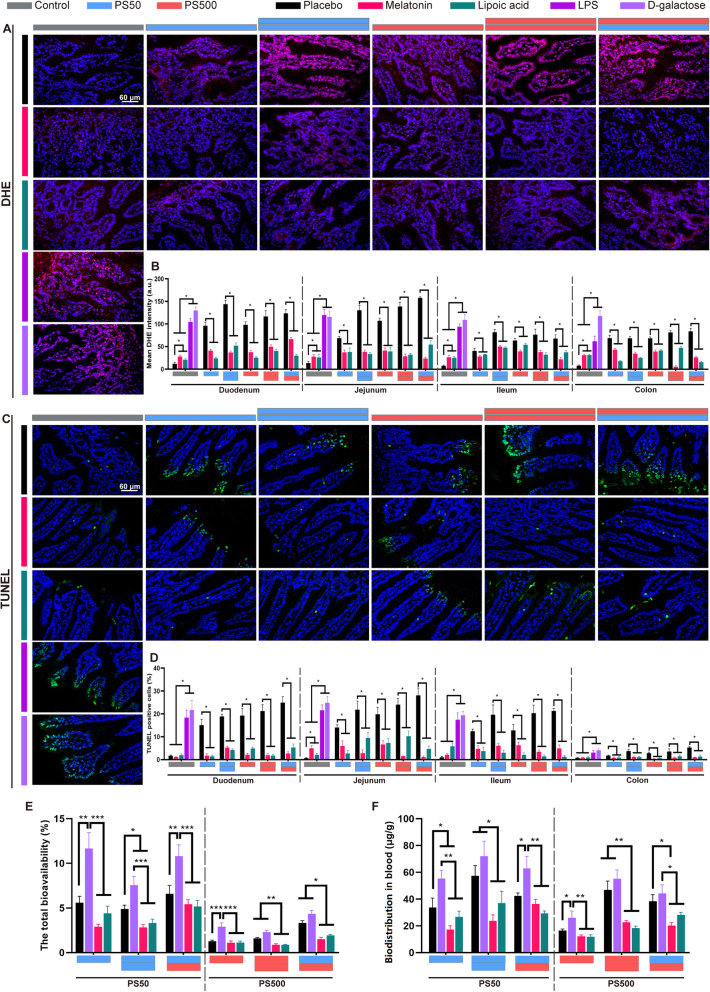
Fig. 6.
ROS neutralization reduced epithelial cell apoptosis and PS particles biodistribution in the intestine. A Representative merged images of the jejunum sections stained with DHE to assess the ROS generation after oxidant or antioxidant treatment. The ROS was stained in red and the nucleus was stained with DAPI in blue. B The quantification of mean DHE intensity in the four intestinal segments was shown. C Representative merged images of the jejunum sections stained with TUNEL to assess the cell apoptosis after oxidant or antioxidant treatment. The apoptosis cells were stained in green and the nucleus was stained with DAPI in blue. D The quantification of TUNEL positive cell rate in the four intestinal segments. E Total bioavailability of PS50 and PS500 after oxidant or antioxidant treatment. F Total accumulation of PS50 and PS500 in the intestine after oxidant or antioxidant treatment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Results were shown as means ± SE. Comparisons were made with ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s method (n = 5 per group). The color bars were used for grouping. The blue and red bar represented a dose of 250 mg/kg body weight for PS50 and PS500, respectively, two bars with same color represented a dose of 500 mg/kg body weight, and two bars with different colors represented the mix exposure group with a dose of 250 mg/kg body weight of each particle