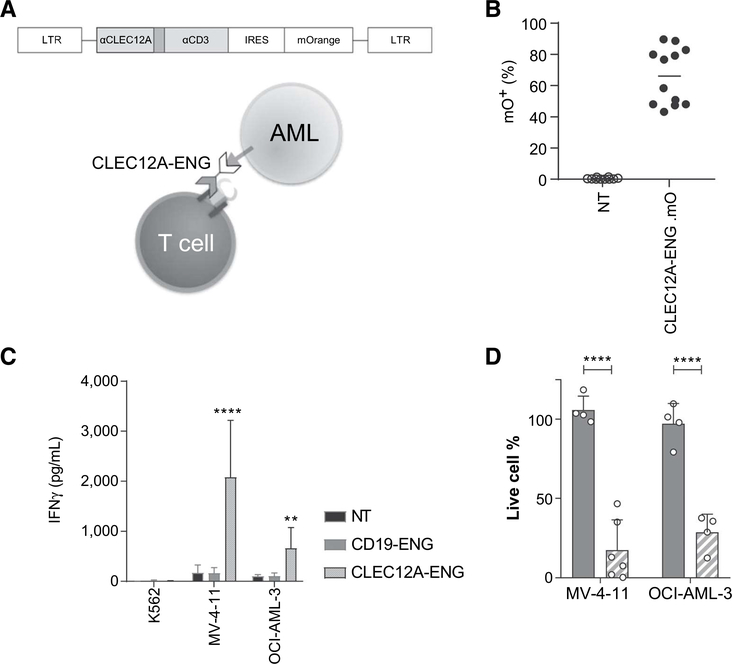
Figure 1.
CLEC12A-targeting with CLEC12A-ENG T cells has specific antileukemic activity in vitro. A, Schematic of construct used for targeting and method of T-cell activation. B, Transduction efficiency of CLEC12A-ENG T cells, (n = 10–12 independent T-cell donors). C, IFNγ secreted by CLEC12A-ENG T cells after overnight culture with CLEC12A−(K562) or CLEC12A+ (MV-4–11, OCI-AML-3) AML cell lines. Unmodified (NT) and CD19-specific T cells (CD19-ENG) included as controls. (n = 4–6 independent donors, difference noted between CLEC12A-ENG and NTT cells.**, P< 0.01; ****,P<0.0001). D, CLEC12A+ (MV-4–11, OCI-AML-3) target cells modified to stably express ffLuc were cultured for 3 days with NT, CD19-ENG (solid bar), or CLEC12A-ENG (striped bar) T cells. D-luciferin was added and live cell percentage determined by BLI. Cells normalized to those in NT T-cell condition. T-cell:target cell ratio was 1:1. Dots representative of individual T-cell donors, (n = 4–6; ****, P< 0.0001).