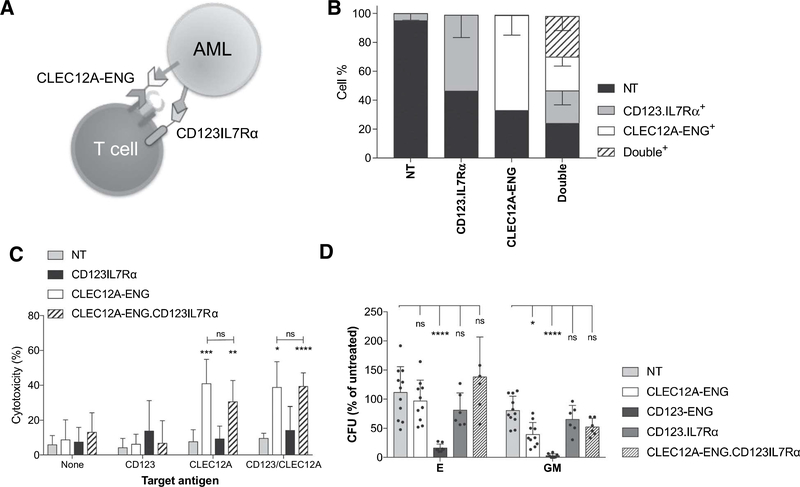
Figure 3.
Coupling of CD123 recognition to IL7R signaling does not cause hematopoietic toxicity. A, Schematic of CLEC12A-ENG.CD123IL7Rα T-cell targeting of CLEC12A+CD123+AML B, Transduction efficiency of NT, singly modified CD123.IL7Rα, CLEC12A-ENG, and dual modified CLEC12A-ENG.CD123IL7Rα T cells. (n = 4 independent T-cell donors). C, Cytotoxicity of T cells versus CLEC12A+, CD123+, or CLECI2A+CD123+ target cells. E:T ratio, 1:5. Significant differences measured in comparison to NTT cells or as indicated, (n = 6 T-cell donors, *, P< 0.05; **, P< 0.01; ***, P< 0.001; ****, P< 0.0001). D, Colony-forming unit (CFU) assays performed with 5:1 ratio of T cells to BMMCs. CD123-ENG T cells used as positive control, (n = 5 BMMC donors, 4 T-cell donors. Data normalized to "no T cell" conditions, differences relative to NT T-cell control (*, P < 0.05; ****, P< 0.0001).