Extended Data Figure 9: Interaction between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and the abundance of highly abundant microbial species in relation to the score of cardiometabolic disease risk.
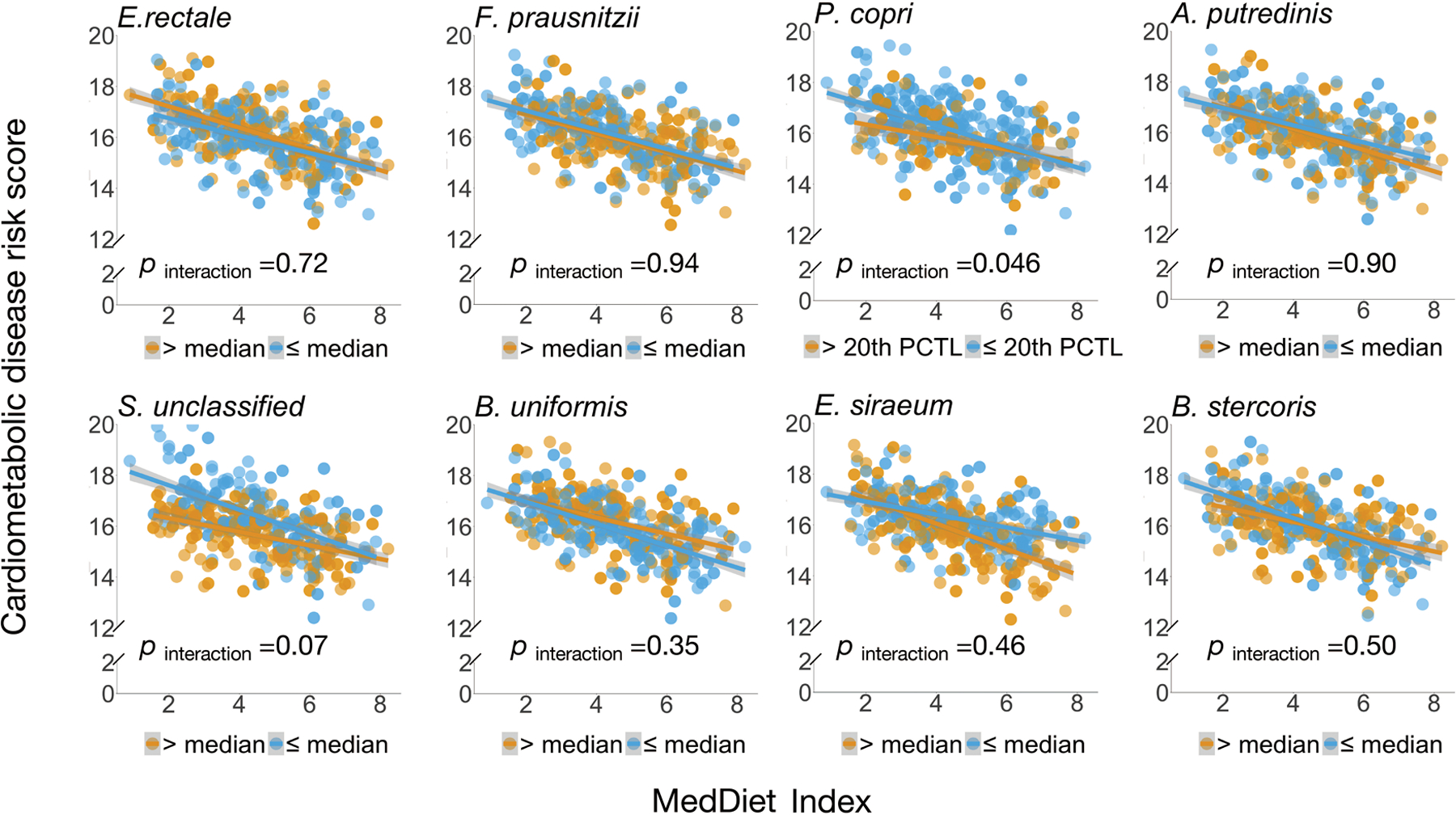
P for interaction was derived from linear mixed models that included participant’s identifier as random effects, the Mediterranean diet index, individual microbial species and their product term, and simultaneously adjusted for total energy intake, age, physical activity level, smoking, probiotic use, Bristol stool scale, and uses of antibiotics, statins, aspirin, proton pump inhibitors and metformin as fixed effects. We performed two-sided likelihood ratio tests by comparing models with and without an interaction term to calculate p-values for interaction (degree of freedom =1). This analysis was based on 468 blood samples from 304 participants. The shaded areas indicate 95% confidence intervals of values on the fitted linear trend lines.
