Figure 2.
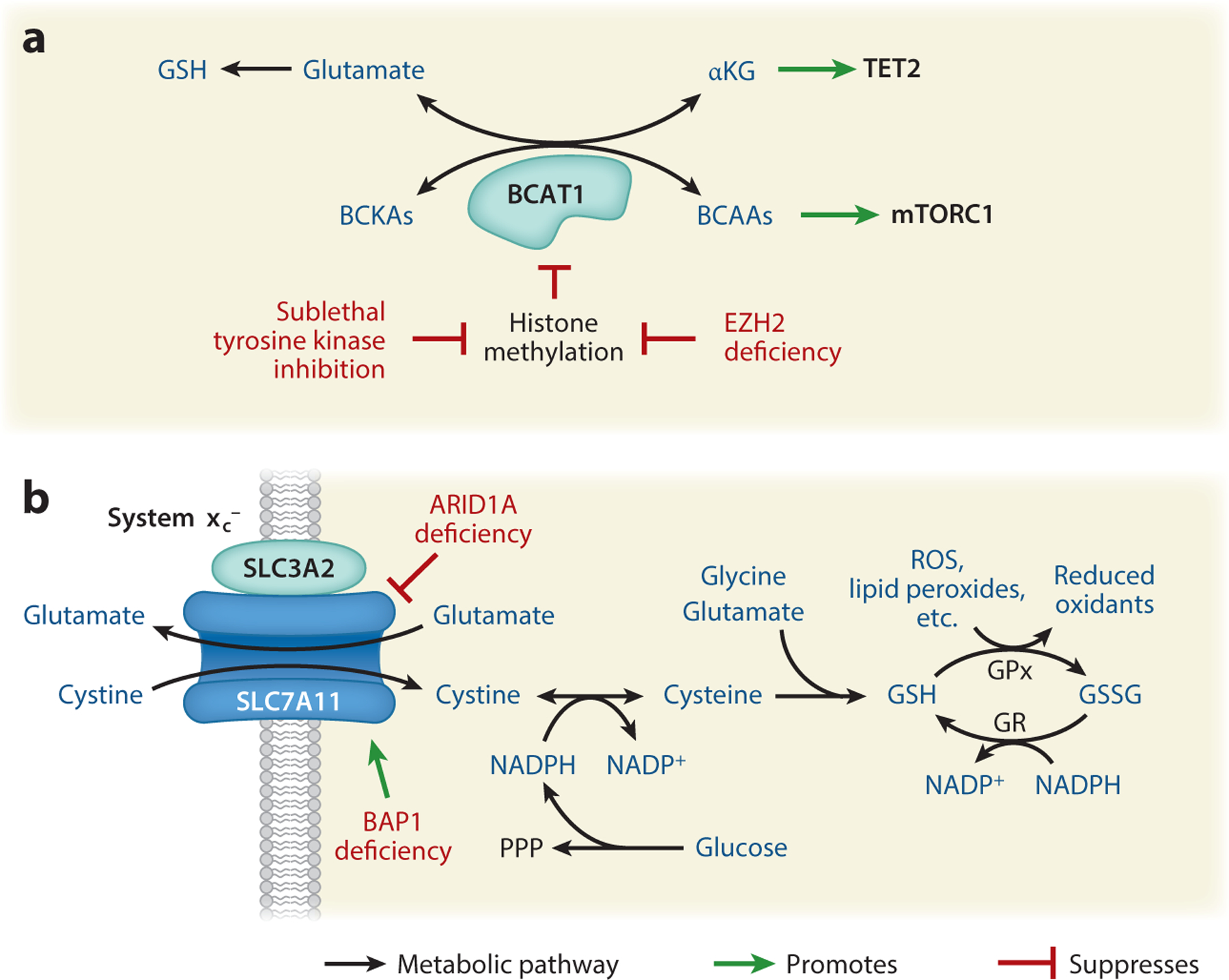
Deficiency in epigenetic enzymes alters expression of metabolic genes. (a) BCAT1 expression is suppressed by histone methylation. Loss of repressive histone methylation occurs with EZH2 deficiency, as well as some cancers treated with sublethal tyrosine kinase inhibition. BCAT1 catalyzes the reversible transamination of BCAAs to BCKAs using αKG as an amino group acceptor and glutamate as an amino group donor. The substrates and products of the reaction catalyzed by BCAT1 impact the generation of downstream metabolites such as GSH and impinge on TET2 and mTORC1 activity. (b) The system xc− cysteine-glutamate antiporter is a dimer of SLC7A11 and SLC3A2. Expression levels of SLC7A11 are regulated by ARID1A and BAP1. System xc− transports intracellular cystine, which is needed to synthesize glutathione. Figure adapted from images created in Biorender. Abbreviations: αKG, alpha-ketoglutarate; BCAAs, branched-chain amino acids; BCKAs, branched-chain alpha-keto acids; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GR, glutathione reductase; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG,oxidized glutathione; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
