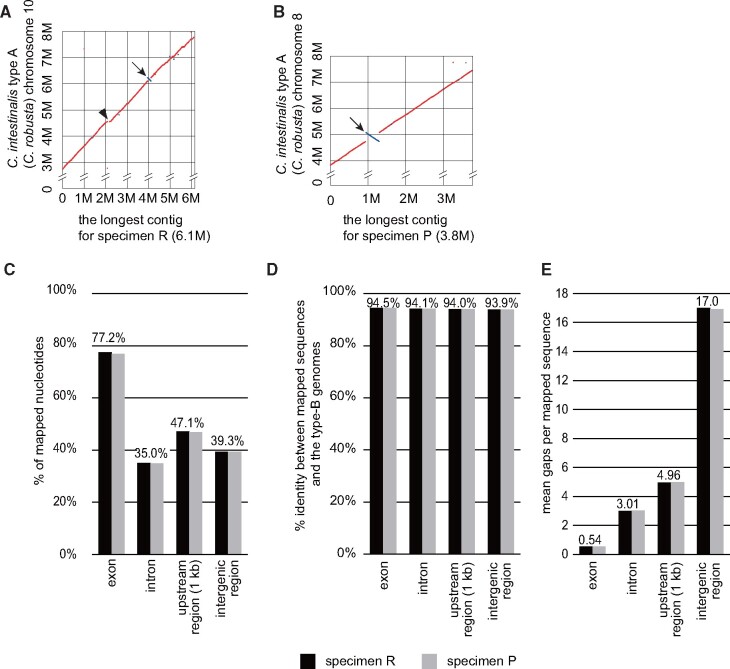
Fig. 1.
Comparisons among genomic sequences for two type-B animals and an inbred type-A animal. (A, B) Alignments of the longest contigs of specimens (A) R and (B) P against type-A chromosomes. An arrowhead indicates an insertion in specimen R, and arrows indicate inversions. Alignments of all contigs with type-A chromosomes are presented in supplementary figure S2, Supplementary Material online. (C–E) Exons, introns, 1-kb upstream regions, and intergenic regions including 1-kb upstream regions of the genome of the type-A HT line were mapped to the genomes of specimens R and P. Proportions of mapped nucleotides (C), nucleotide identities in mapped regions (D), and mean gap numbers per sequence (E) are shown.