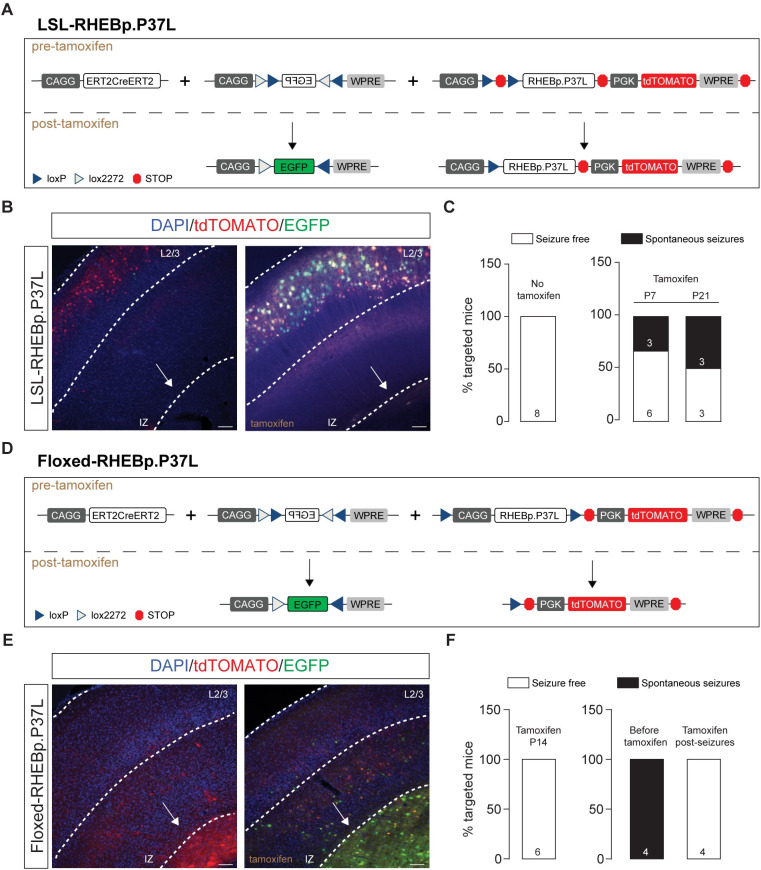
Fig 4. The heterotopic nodule is neither necessary nor sufficient to induce spontaneous seizures.
(A and D) Schematic representation of the DNA plasmids used in the experiment. The LSL or the floxed construct was expressed in combination with the CAGG-ERT2CreERT2 and a CAGG-DIO-EGFP constructs. The EGFP in the CAGG-DIO-EGFP construct is expressed only upon tamoxifen injection, providing a measure of efficient cre-dependent recombination (see representative images in B and E). (B) Representative images showing efficient cre recombination upon tamoxifen administration in adult mice injected in utero with the LSL construct; note the absence of heterotopic nodule (indicated by the white arrow). (C) Bar graphs indicating the percentage of targeted mice showing seizures after injection at either P7 or P21 for 4 consecutive times with tamoxifen and measured with EEG until 12 weeks of age; numbers in the bar plots indicate the number of mice. (E) Representative images showing efficient cre recombination upon tamoxifen administration in adult mice injected in utero with the floxed construct; note the presence of heterotopic nodule (indicated by the white arrow). (C) Bar graphs indicating the percentage of targeted mice showing seizures after injection at either P14 or upon seizure development for 4 consecutive times with tamoxifen and measured with EEG until 12 weeks of age; numbers in the bar plots indicate the number of mice. Scale bars: 100 μm. The data underlying this figure can be found in S4 Data. EEG, electroencephalography; LSL, Lox-Stop-Lox.