Fig. 1:
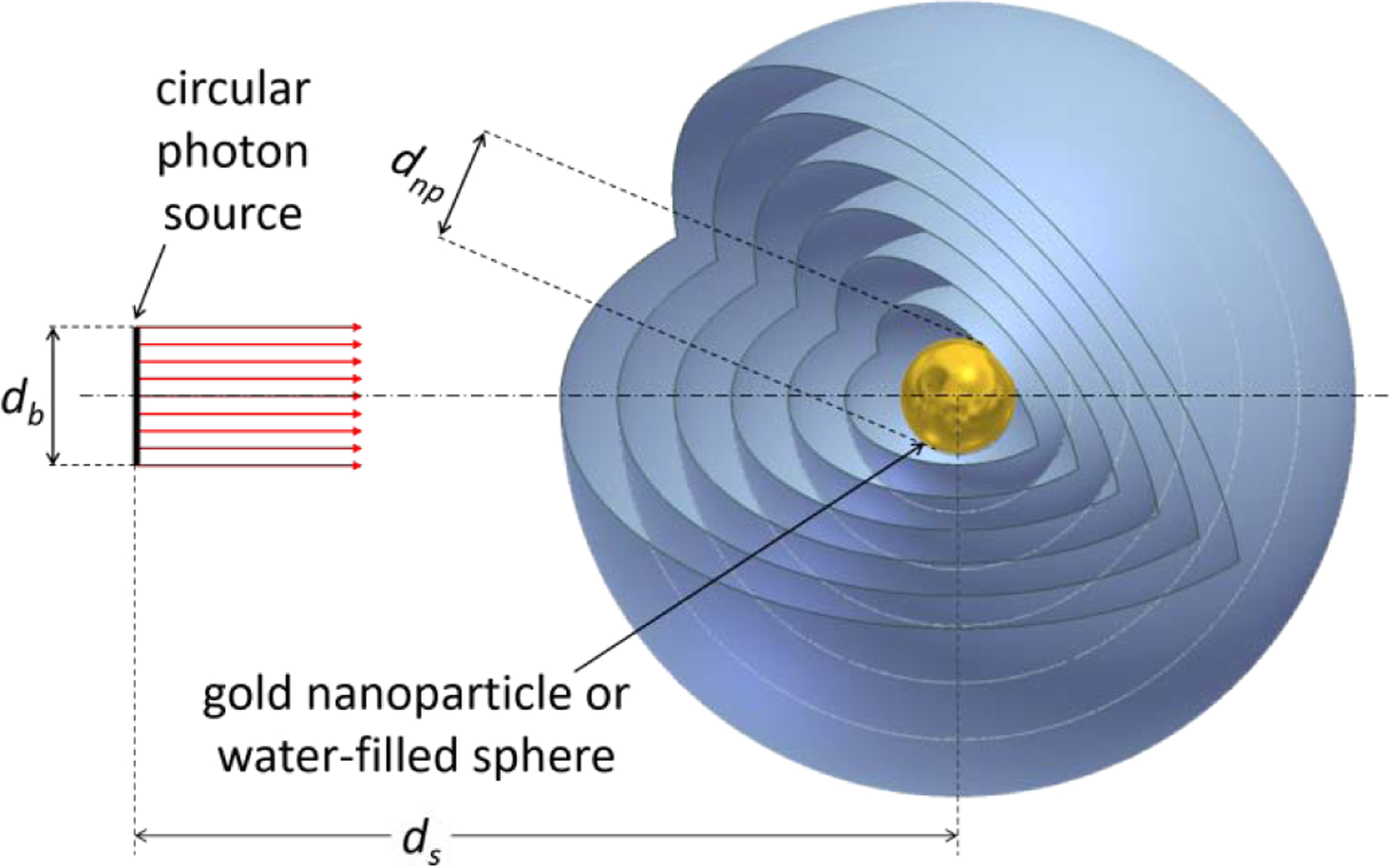
Schematic illustration of the geometry setup for the simulations. A homogeneous circular X-ray source of diameter db emits photons along its rotational symmetry axis (dot-dashed line). Energy deposition is scored in concentric spherical shells around a sphere of diameter dnp located at a distance ds = 100 μm from the photon source. This sphere is filled with either gold or water; the rest of the geometry is filled with water. The first 100 spherical shells have a radial thickness of 10 nm; the remaining 49 spherical shells have a radial thickness of 1 μm. The diameter of the photon source is db = dnp + 10 nm; the diameter of the central sphere (gold nanoparticle) is either 50 nm or 100 nm.
