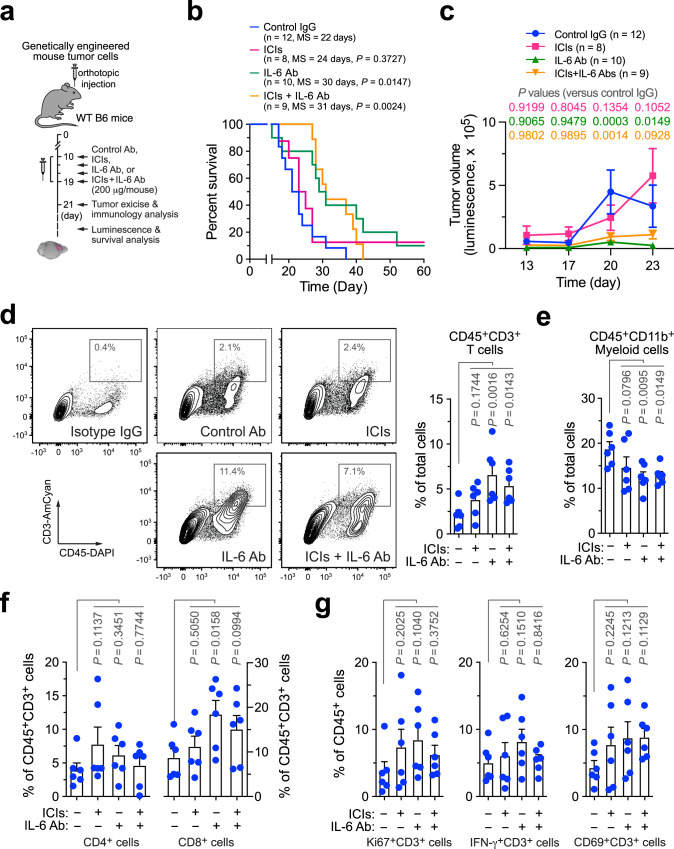
Fig. 2. IL-6 neutralization enhances T-cell infiltration into GBM tumors and improves animal survival but does not sensitize tumor to immune checkpoint blockade.
GBM was induced in WT B6 mice, followed by injection with control IgG, anti-IL-6 antibody (Ab), immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), or ICIs plus anti-IL-6 Ab. a Schematic approach. b, c Survival and tumor growth analyses (n = 8–12 mice, specific n numbers are shown in the figure). b Mouse survival was monitored for 60 days and subjected to two-sided log-rank Mantel–Cox analysis. MS, median survival. c Tumor volume was analyzed by bioluminescence imaging during days 13–23 (mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. d–g Tumors were excised 2 days after treatment. Tumor-derived single-cell suspensions were stained with antibodies against CD45, d CD3, e CD11b, f CD4, CD8, CD3, and g Ki67, IFN-γ, and CD69, followed by flow cytometry analyses. d Analysis for CD3+ T cells. Left, representative cell sortings. Right, quantified results (n = 6 mice, mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test. e–g Quantified results for immune cells (n = 6 mice, mean ± SEM). Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test. Source data are provided as a Source data file.