FIGURE 7.
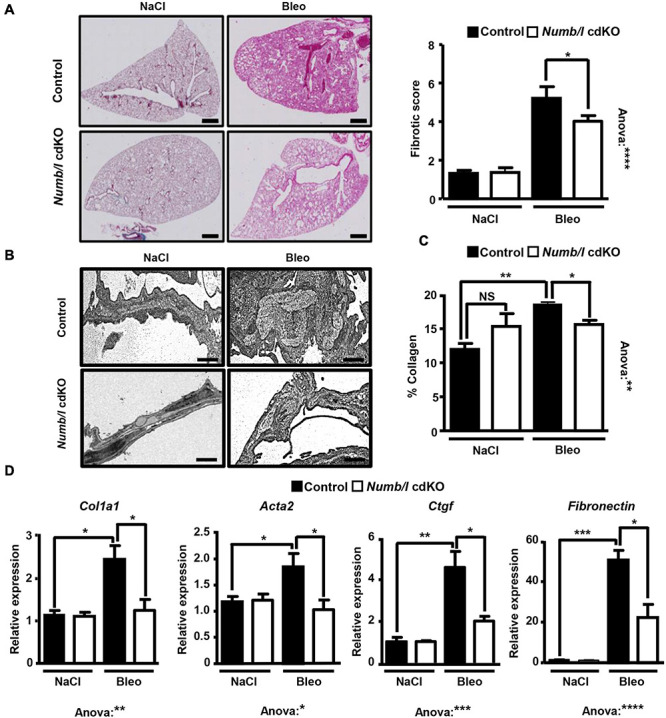
Inactivation of Numb/l in lung epithelial cells ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. (A) H&E staining of paraffin sections (5 μm) from Numb/l cdKO vs. control mice 21 days after bleomycin treatment. Scale bar = 1 mm. Quantification of the fibrotic foci is on the right. The fibrotic score was assigned arbitrarily between 0 (non-fibrotic) and 8 (highly fibrotic) using randomly chosen H&E-stained slides from control and Numb/l cdKO mice (control: n = 3; Numb/l cdKO: n = 5; *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001). (B) Electron microscopy analysis of collagen I fiber deposition in control and Numb/l cdKO animals 21 days after treatment with vehicle (NaCl) or bleomycin (Bleo). Scale bar = 1 μm. (C) Sircol-based analysis of collagen content in whole-lung homogenates derived from control and Numb/l cdKO animals (n = 4; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; NS, not significant). (D) RT-qPCR analysis of pro-fibrotic genes in lung homogenates from control and Numb/l cdKO animals (control: n = 3; Numb/l cdKO: n = 5; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).
