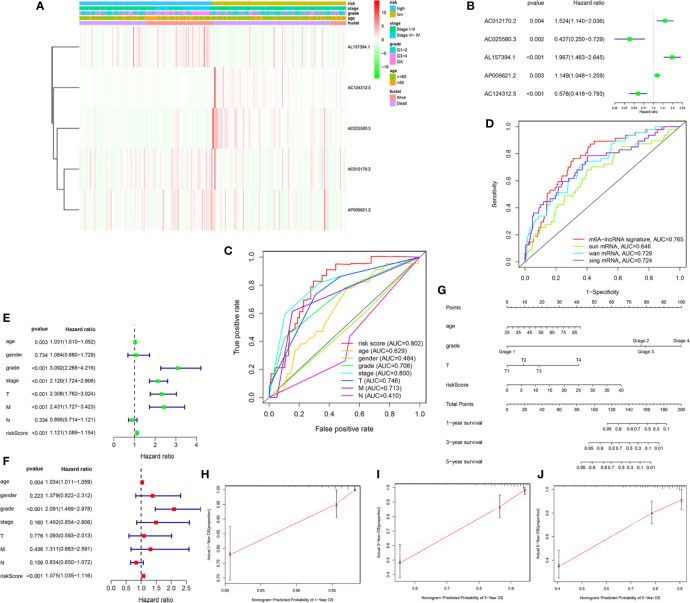
Figure 4.
Estimation of clinical Value of the m6A-related lncRNAs prognostic risk signature in KIRC patients. (A) The heatmap showed associations between the expression of the five m6A-related lncRNAs in the low- and high-risk group and clinicopathological features, including survival status (alive or dead), age (>60 y or <=60 y), AJCC stages (stages I–II or III–IV), and AJCC grade (1–2, 3–4, or NA) (all p < 0.05) in training set. (B) The forest plots showed the prognostic ability of the five m6A-related lncRNAs in the prognostic risk model (p < 0.05). (C) The multivariate receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showed predictive accuracy of risk score was higher than other clinicopathological features. (D) Multivariate ROC curves showed the sensitivity and specificity of the prognostic risk signature were higher than other published biomarkers in predicting the prognosis of KIRC patients. (E) The univariate Cox regression analysis showed that risk score and clinicopathological features, included age, grade, AJCC stage, T and M stage were prognostic-related variables. (F) The multivariate Cox regression analysis showed risk score, grade, age were independent prognostic factors. (G) Construction of a prognostic nomogram based on risk score and prognostic-related clinicopathological parameters to predict 1-, 3-, 5-year overall survival of KIRC patients. (H–J) The calibration curves of the nomogram displayed the concordance between predicted and observed 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS.