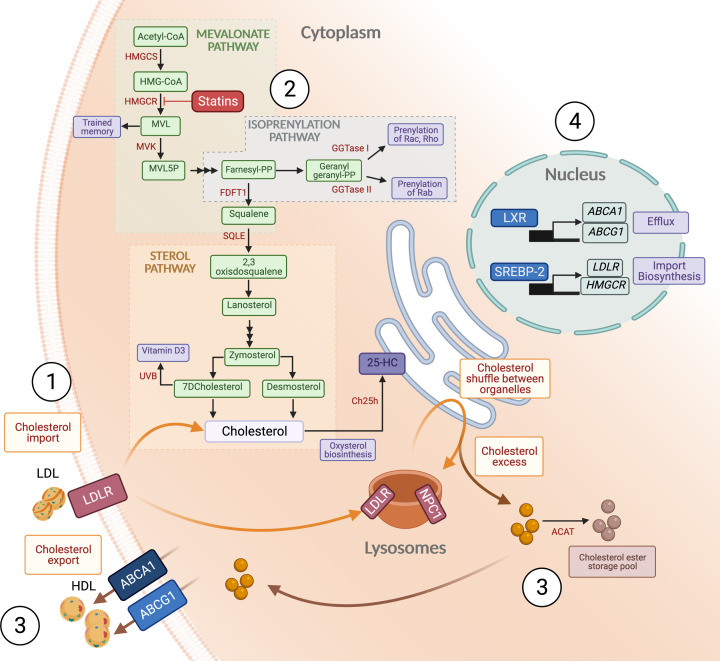
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the cellular cholesterol metabolism.
1. Cholesterol is sourced from import of LDL through LDLR; 2. The cholesterol biosynthesis pathway and its branches: the mevalonate pathway, the isoprenylation pathway and the sterol pathway. Some important functions in immune cells are highlighted in purple; 3. Excess cholesterol can be transformed into cholesterol esters or exported through HDL; 4. Cholesterol homeostasis is maintained at the transcriptional level by the actions of SREBP-2 and LXR. Statins inhibit the activity of HMGCR. Abbreviations: 25HC, 25-hydroxycholesterol; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter 1; ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 1; ACAT, acyl coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase); Ch25h, cholesterol 25-hydroxylase; FDFT1, farnesyl diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1 or squalene synthase; GGTase, geranylgeranyl transferase; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A; HMGCS, MHG-CoA synthase; HMGCR, MHG-CoA reductase; LDL, low density lipoproteins;LDLR, LDL receptor; LXR, liver X receptor; MVK, mevalonate kinase; MVL, mevalonate; MVL5P, mevalonate-5-phosphate; NPC1, Nieman-Pick C 1; SQLE, squalene epoxidase; SREBP-2, sensor response element binding protein 2.