Figure 2.
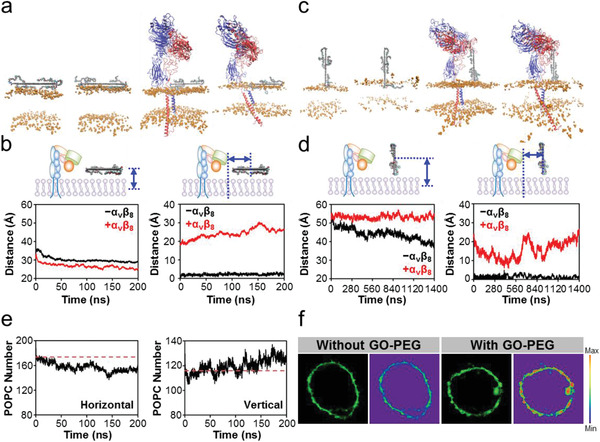
Effects of GO‐PEG on POPC membrane in the horizontal and vertical mode of ternary model. a) Structure at the initial and terminal moments of production simulation in the horizontal mode. GO‐PEG is placed in the same horizontal position. Blue, α v subunit; Red, β 8 subunit; Orange, head piece of POPC lipids; Other, GO‐PEG. The membrane is simplified as the area between the head of POPC lipids to facilitate the observation of changes in the membrane. b) Vertical‐ and horizontal‐centroid distances between GO‐PEG and POPC membrane in the horizontal mode. GO‐PEG is adsorbed on POPC membrane surface and maintains a relatively stable state. c) Structure at the initial and terminal moments of production simulation in the vertical mode. GO‐PEG is placed in the same horizontal position. The legend descriptions refer to those in (a). d) Vertical‐ and horizontal‐centroid distances between GO‐PEG and the POPC bilayer. α v β 8 inhibits the extraction of vertical GO‐PEG‐induced POPC membrane lipids and mediates a three‐step horizontal motion of POPC membrane lipids. e) Number of POPC membrane lipids within 4 nm of GO‐PEG in the production simulation of ternary model. Left panel: horizontal mode; Right panel: vertical mode. POPC membrane lipids clustered with GO‐PEG in the vertical mode. f) Representative fluorescence imaging on lipid aggregation of macrophage with and without GO‐PEG stimulation. The membrane lipids were labeled with lipophilic β‐BODIPY dye.
