Figure 11.
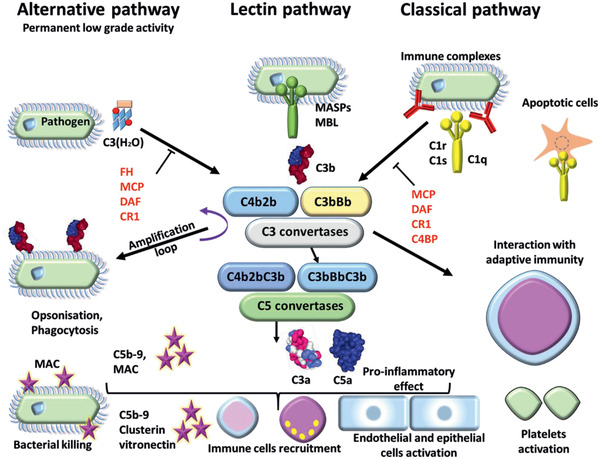
Complement activation. Complement system is composed of three different pathways. The classical pathway (CP) is activated by immune complex formation on pathogen surface and by calreticulin expressed on apoptotic cells, leading to C1 complex association. The LP recognizes mannose‐terminating glycan on pathogens leading to MBL MASP complex activation. Both induce formation of the classical C3 convertases C4b2b. The AP is permanently activated at low level by spontaneous hydrolysis of C3 into C3 (H2O). Lack of complement inhibitor on pathogens induces alternative C3 convertase activation C3bBb. Complement activation leads to opsonization and phagocytosis by C3b deposition, bacterial lysis by C5b–9 complex formation and inflammation by recruitment of immune cells, endothelial and epithelial cell activation, and platelet activation. Membrane cofactor protein (MCP), decay accelerating factor (DAF), complement receptor 1 (CR1), and C4 binding protein (C4BP) inhibit the complement activation by the classical pathway. DAF, MCP, CR1, and Factor H inhibit the complement activation by the AP.
