Fig. 3.
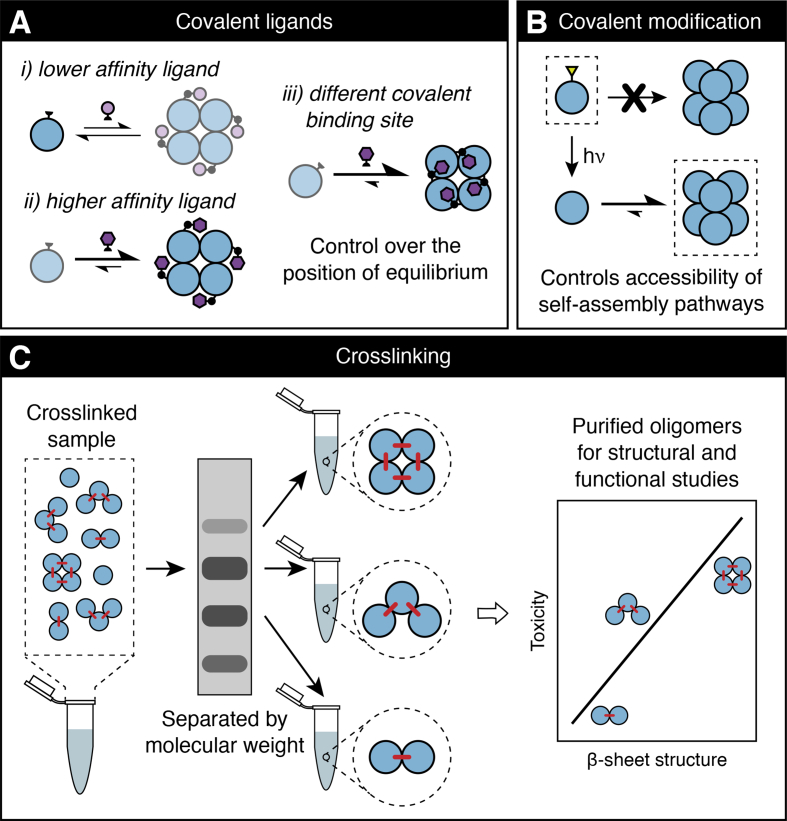
Covalent strategies for the control of oligomer populations in amyloid protein samples. A: Covalent ligands have been shown to be powerful modulators of oligomerization equilibria and can allow oligomer distributions to be tuned based on the affinity and location of the protein-ligand interaction [27]. B: The use of photolabile groups (e.g. N-2-nitrobenzyl) to sterically or chemically prevent amyloid proteins and peptides from accessing particular regions of the self-assembly landscape can allow oligomer populations to be controlled in a UV-dependent manner [30]. C: Covalent crosslinking using the PICUP or diazirine-based approaches represents a means of trapping a distribution of oligomers formed by a self-assembling protein, and the resulting crosslinked species can be separated (e.g. by SDS-PAGE, or using other, higher-throughput size/mass separation approaches) for individual structure and toxicity studies [[239], [240], [241]].