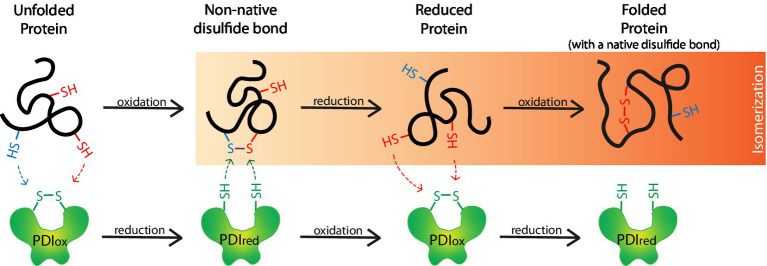
Figure 3.
Protein disulfide isomerases (PDIs) form disulfide bridges that assist in the proper folding of proteins. PDIs (PDIox) oxidize thiol/sulfhydryl (–SH) side chains on unfolded proteins to form disulfide bonds (S–S) and are thereby reduced (PDIred). S–Ss often form between incorrect thiols (i.e., blue-SH with a red-SH) to form non-native S–Ss. When this occurs, the S–S undergoes isomerization whereby non-native S–Ss are reduced back to-SHs by a PDIred. A PDIox then oxidizes the correct-SHs (i.e., 2 red-SHs) on the reduced protein to form the correct native S–S and produce a properly folded protein.