Fig. 2. Gef26 plays a role in NMJ development.
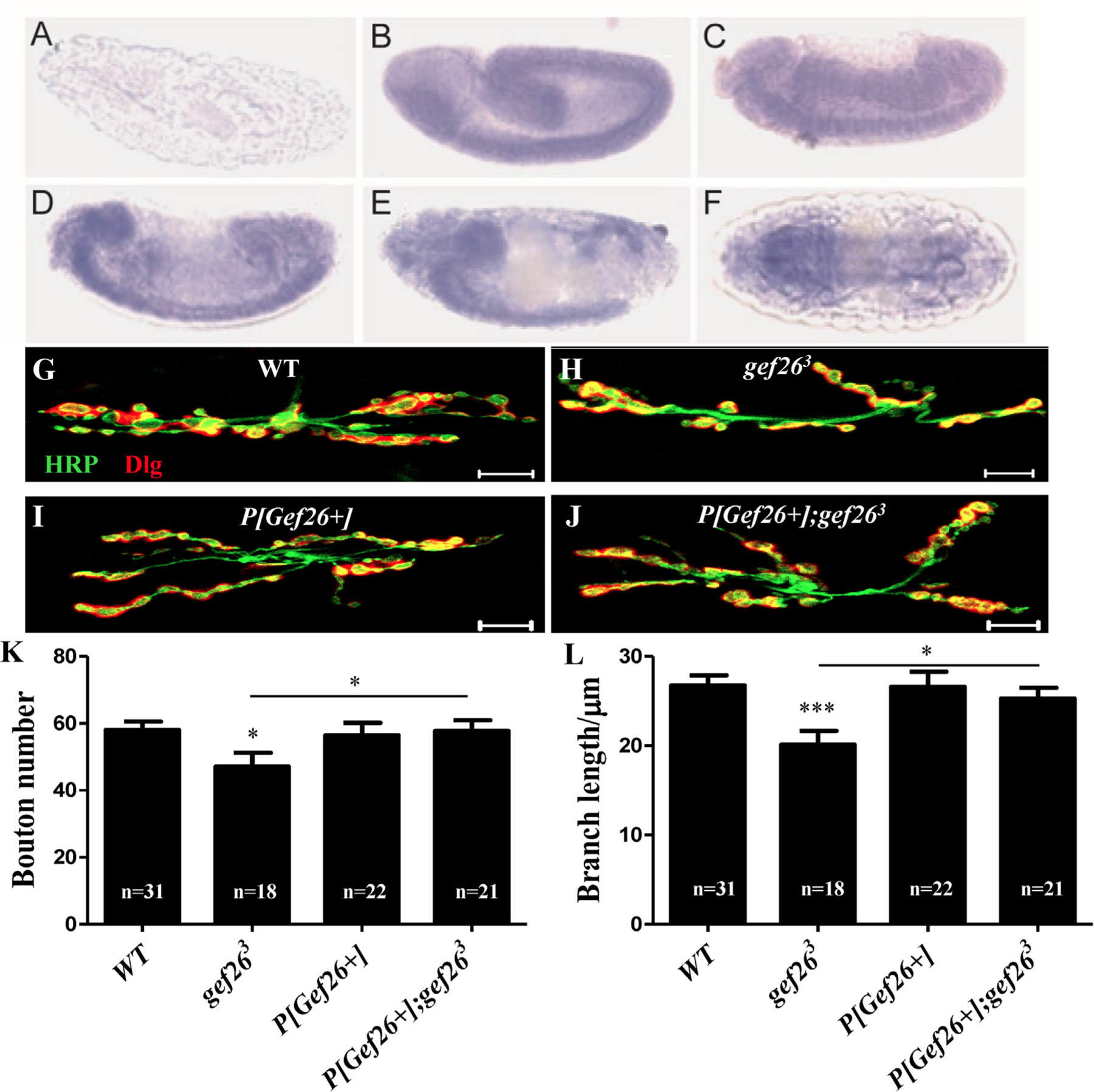
(A-F) RNA in situ hybridization showed spatial distribution of Gef26 transcript in embryos. Embryos were oriented with anterior to the left. Lateral view of negative control showed no staining detected with sense probe (A). Lateral view of stage 13 (B), 14 (C), 15 (D), and 16 (E) embryos showed staining in the developing brain and ventral nerve cord (VNC). (F) Dorsal view of a stage 16 embryo showed expression of Gef26 on ventral nerve cord. (G-J) Representative morphology of NMJ 6/7 of second-instar larvae in WT, gef263, P[Gef26+], and the rescue line. Scale bars = 10 µm. (K-L) Quantification of bouton number and branch length of NMJ6/7 in the indicated lines in G-J. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
