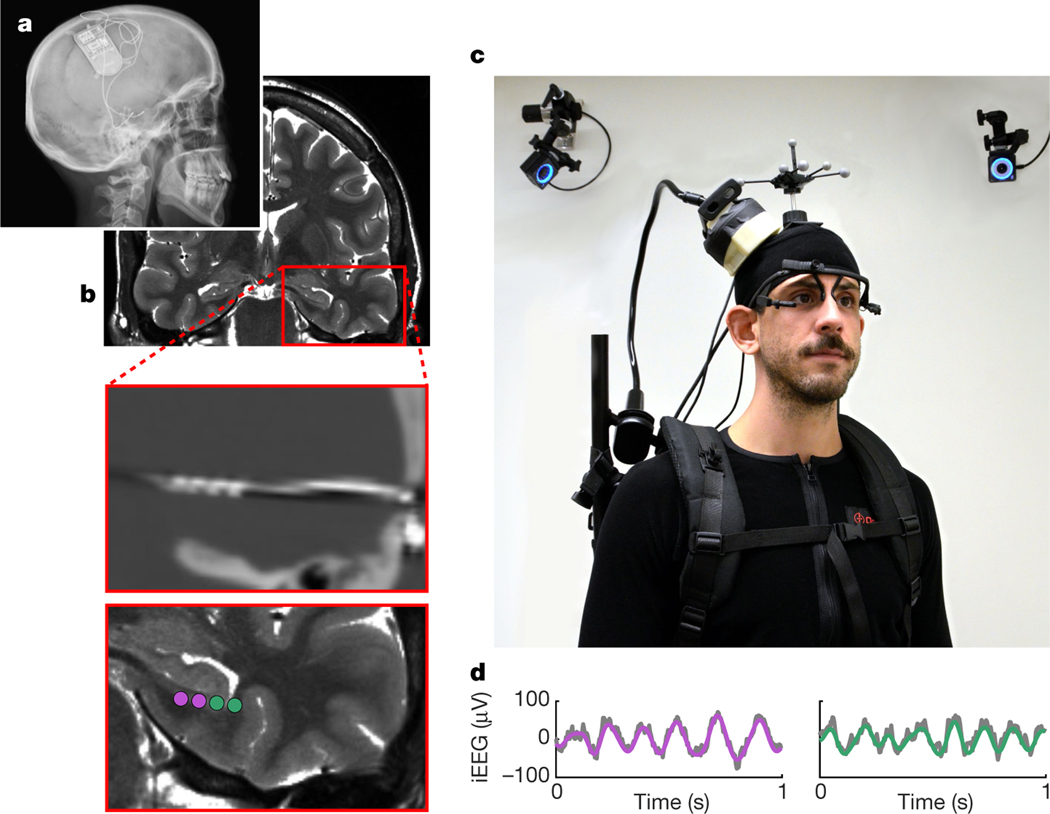
Fig. 1 |. RNS System and experimental setup.
a, X-ray image of a participant with a chronically implanted RNS System (NeuroPace Inc.). b, Preoperative magnetic resonance image (top), co-registered with a postoperative computed tomography image showing an implanted depth electrode (middle), and contact locations of two bipolar recording channels (bottom). c, iEEG data were continuously recorded with a NeuroPace Wand that was secured on a participant’s head, allowing the participant to freely walk around during recordings. Their position was tracked via motion-tracking cameras and reflective markers on the participant’s head. Eye movements were tracked with a mobile eye-tracking headset. Shown is an experimenter, rather than an actual participant, wearing the full setup for illustrative purposes. d, Example raw iEEG signal (grey) from two recording channels, overlaid with bandpass-filtered low-frequency oscillations (purple and green; 3–12 Hz).