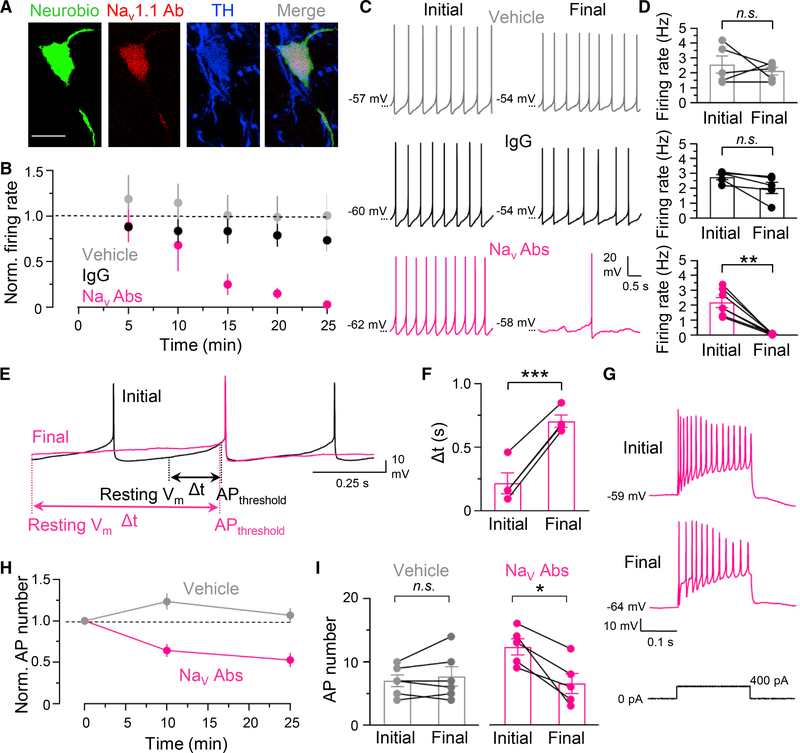
Figure 2. Single-cell application of Nav Abs inhibits SNc DA neuron activity and decreases excitability.
(A) Nav1.1 Ab (secondary antibody only) and TH immunostaining in SNc after whole-cell recording; Nav1.2 Ab immunostaining is illustrated in Figure S1B. Neurobiotin 488 was introduced with Nav1.1 Ab via the recording pipette (n = 5 slices). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(B) Time course of spontaneous SNc DA neuron firing frequency over 25 min with intracellular application of vehicle (n = 5), IgG (n = 5), or Nav1.1 Ab + Nav1.2 Ab (Nav Abs) (n = 7).
(C) Spontaneous activity with vehicle, IgG, or Nav Abs in the pipette.
(D) Summary of Nav Ab effects on spontaneous frequency (vehicle, 99% ± 23% of initial frequency, n = 5, p = 0.5; IgG, 79% ± 13%, n = 5, p = 0.15; Nav1.1 Ab and Nav1.2 Ab, 14% ± 5%, n = 7, **p < 0.01; paired t test).
(E) Spontaneous activity with Nav Abs in the pipette; Δt is the time from resting membrane voltage (Vm) to AP threshold (APthreshold).
(F) Quantification of Δt when recorded with Nav Abs in the pipette (initial, 0.22 ± 0.07 s; final, 0.71 ± 0.04 s, ***p < 0.001). Bars are means ± SEM for n = 4; paired t test.
(G) Response of SNc DA neurons recorded in current clamp during depolarizing current injection (+400 pA, 200 ms) after establishing whole-cell recording (initial) and the end of 25-min recording (final) with Nav Abs in the pipette. Intracellular application of Nav Abs decreased the number of APs evoked by current injection.
(H) Time course of the effect of single-cell application of Nav Abs on AP number evoked during current injection (vehicle, n = 6; Nav Abs, n = 5).
(I) AP number during current injection with vehicle or Nav Abs in the pipette (vehicle, 106% ± 9% of initial, n = 6, p = 0.4; Nav Abs, 64% ± 7%, n = 5, *p < 0.05; paired t test).