Figure 2:
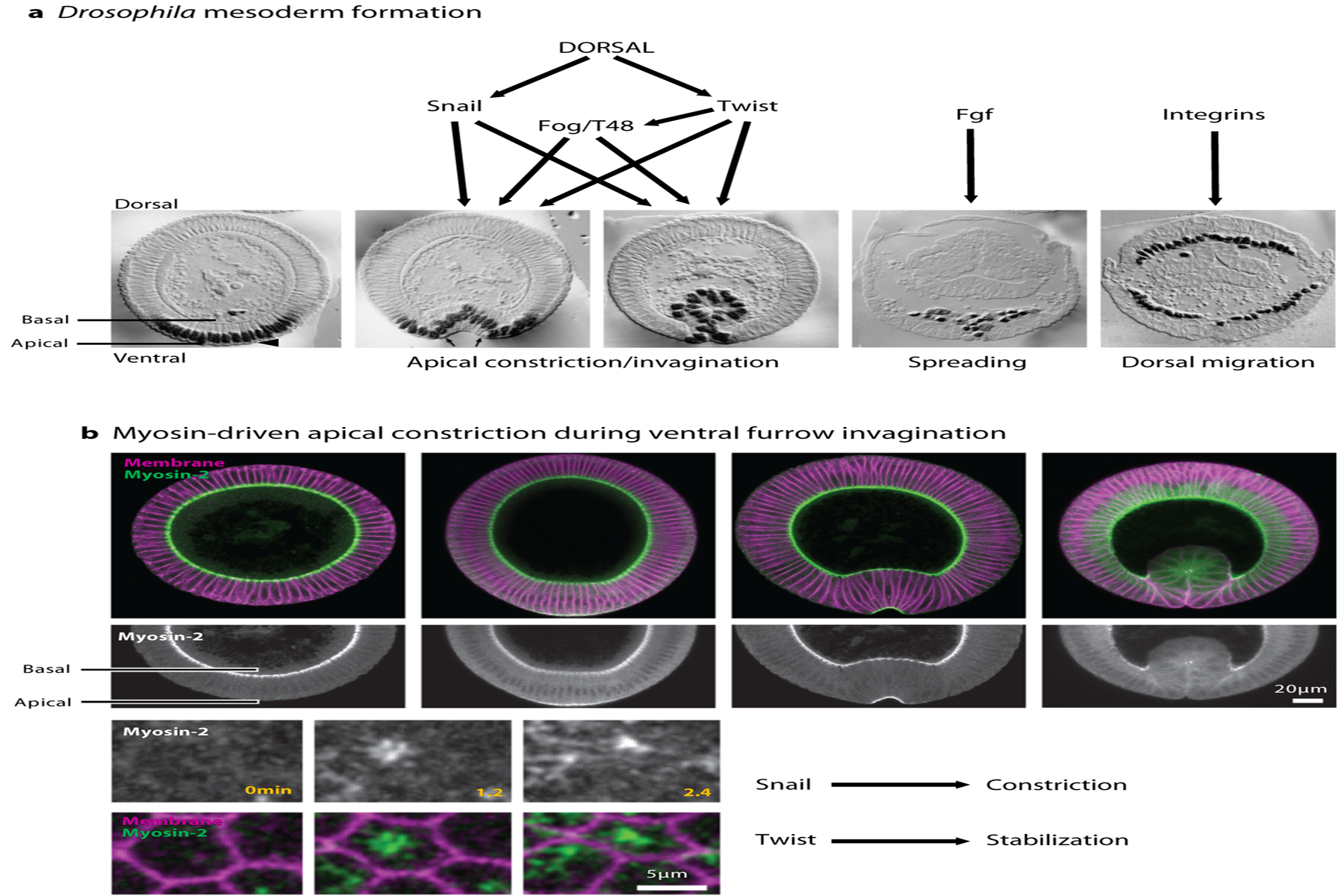
Drosophila mesoderm formation during gastrulation. (a) Drosophila embryo sections at different stages during gastrulation, showing apical constriction and invagination of the ventral cells that will make the mesoderm, as well as spreading and dorsal migration of mesodermal cells after EMT. Black nuclei represent Twist immunostaining. Panel adapted with permission from Leptin & Grunewald (1990). (b) Myosin-2 accumulates on the apical side of ventral furrow cells and triggers apical constriction. Apico-medial accumulation of Myosin regulates pulsed apical constriction that leads to invagination. Snail controls the constriction phase and Twist stabilizes the apical surface. Figure adapted with permission from Vasquez et al. (2014).
